Gene Network Analysis Reveals Functional Drivers of Age-Associated Disorders
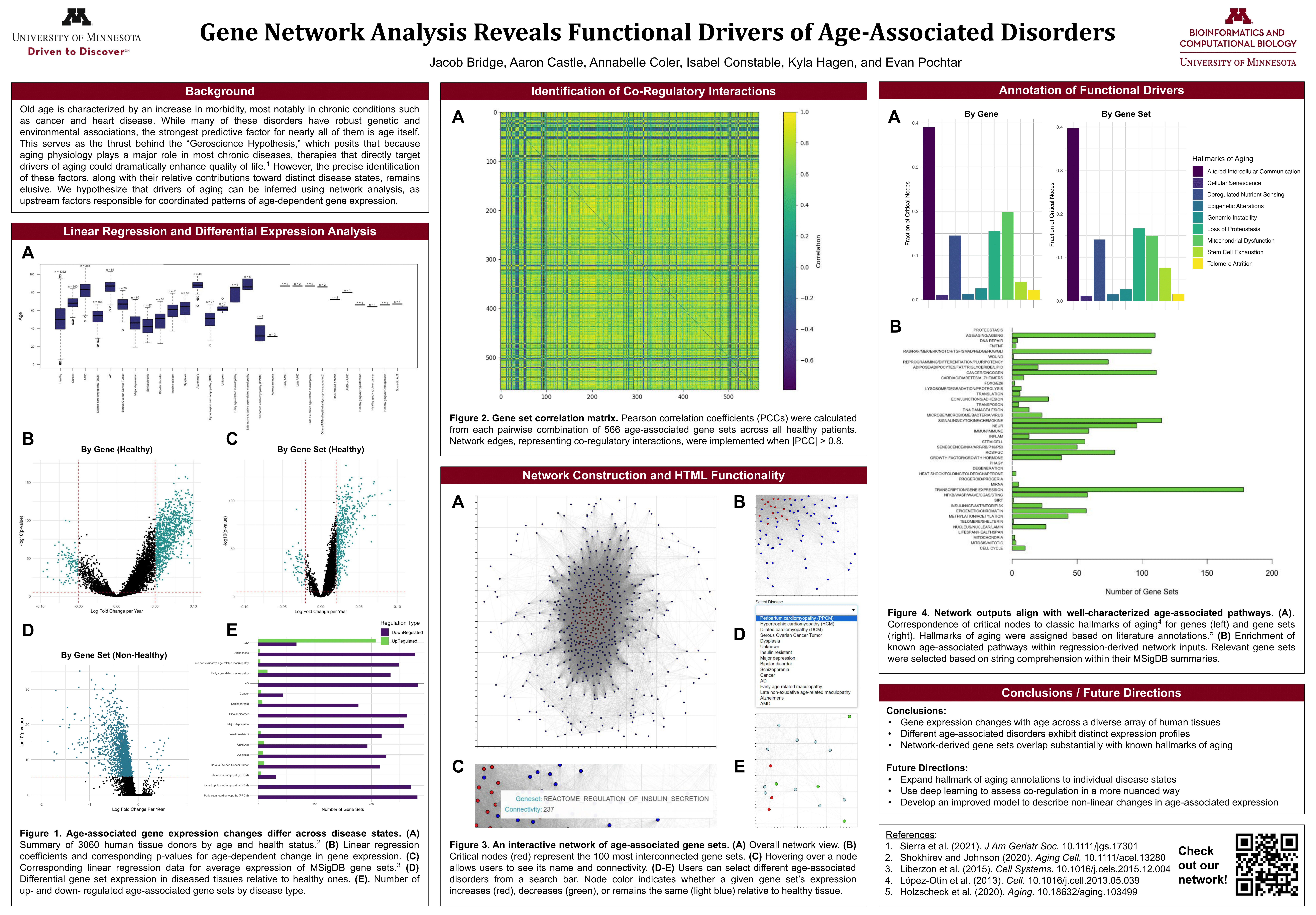
This project involved developing a computational pipeline to analyze age-associated gene expression changes and their relationship with various diseases using RNA-seq data. Raw data was normalized to control for sequencing depth, library size, and gene length, followed by variance stabilization and batch correction. Tissue-independent age effects were modeled using multiple linear regression, with curated gene sets from the Molecular Signatures Database employed to explore functional pathways. Differential expression analyses identified disease-specific alterations, while network analysis revealed co-regulatory interactions between gene sets. These preprocessing steps were done in R, while the actual visualizations and network creations were done in Python. These interactive visualizations of gene networks featured dynamic filtering and annotation of hallmark aging processes, providing insights into the molecular drivers of aging and disease.
Calculating Depth Using a Neural Radiance Field
In this project, I optimized Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) models to improve depth estimation and computational performance. Using datasets such as the TinyNeRF Lego excavator and custom Blender-generated scenes, I developed Python scripts to preprocess data, generate depth maps, and convert outputs into NeRF-compatible formats. Transitioning from TensorFlow to PyTorch and integrating various NeRF algorithms, including TinyNeRF and DexNeRF, led to significant speedups—achieving a 5.4x improvement over the original TinyNeRF. This especially was the hardest part of the project, as runs often took over two hours, and various forms of error handling had to be implemented to avoid terminating in the middle of runs. Hyperparameter tuning was another critical part of the project, as I learned how easily neural networks can be helped or harmed with the wrong parameters. Additionally, I compared NeRF-based depth estimation against other state-of-the-art methods like MiDaS and Stereo Vision, evaluating their performance through structural similarity, mean absolute error, and mean squared error metrics. The project highlighted NeRF's potential for depth estimation while providing insights into its limitations compared to other depth generating algorithms.
From Handwritten Math to Latex: A Deep Learning Approach with Error Correction
This project presents a novel hybrid approach for converting handwritten mathematical expressions into syntactically correct LaTeX code. We combine an image-to-LaTeX model with a language-model-based postprocessor to address the challenges of accurately recognizing complex mathematical notation. Our system comprises a ResNet-34 based CNN encoder for feature extraction from handwritten images, a Transformer decoder for LaTeX sequence generation, and a finetuned Phi-4-mini language model for syntax correction. Trained on the MathWriting dataset with data augmentation techniques, our model achieves 85.59% accuracy with beam search decoding alone, increasing to 86.22% with LLM post-processing. This work provides a foundation for future improvements in mathematical content recognition systems for educational and research applications.
ElevateVR Drone Simulator: An Affordable First Person View Drone Simulator
Collaborated with a team to design and implement ElevateVR Drone Simulator, an immersive first-person-view (FPV) drone simulation experience built in Unity. Leveraged Unity's physics engine to model realistic drone dynamics, incorporated cybersickness reduction techniques, and designed detailed virtual environments to enhance user engagement. The project addresses the lack of affordable, high-fidelity FPV simulators, providing a practical and accessible tool for drone enthusiasts and professionals. Delivered the project on schedule, showcasing strong teamwork, technical skills, and a commitment to quality user experiences.
Optimizing Small Language Models for Cryptographic Applications
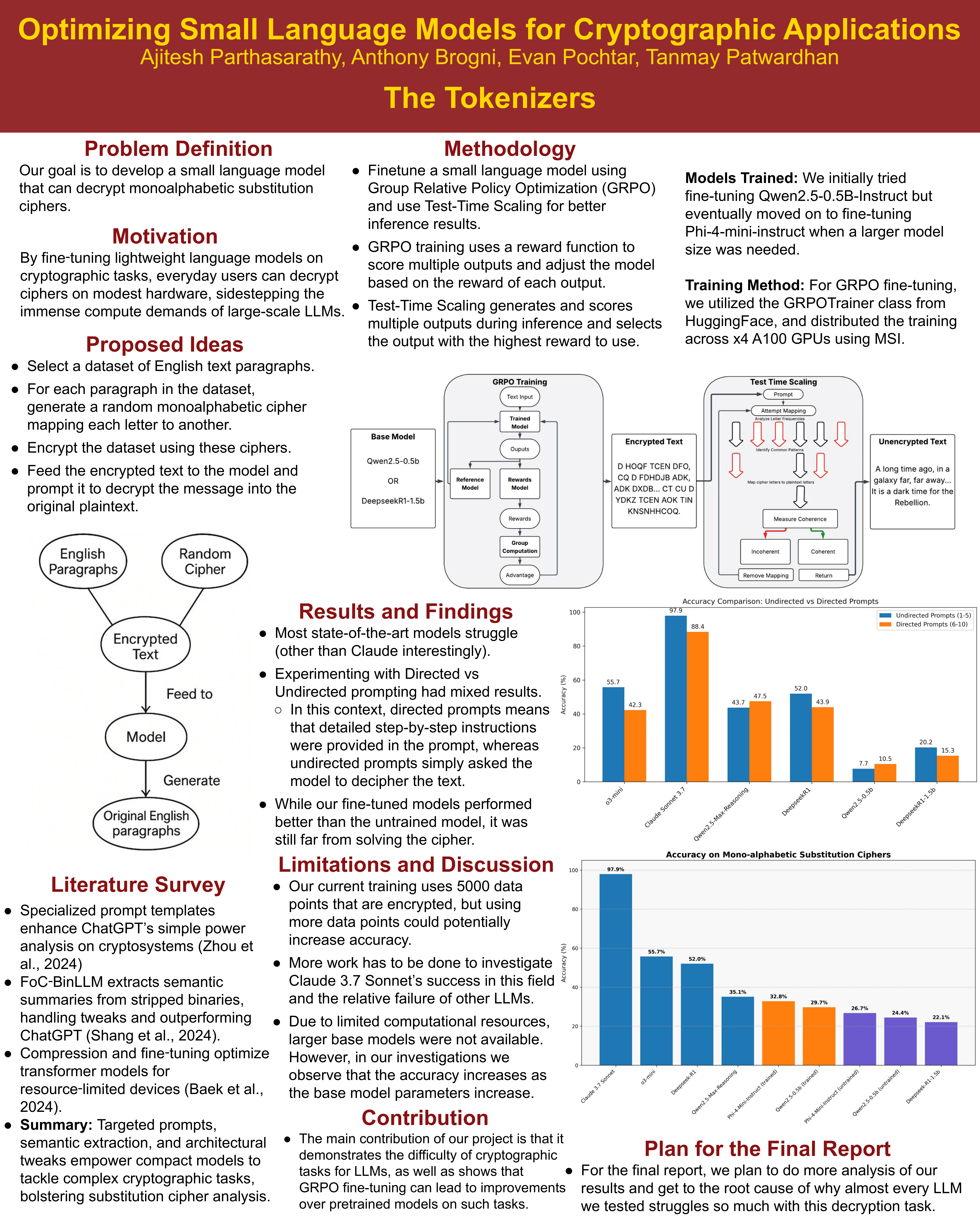
We present a targeted investigation into the ability of fine-tuned small language models (SLMs) to break mono-alphabetic substitution ciphers. Using Qwen2.5-0.5B and Phi-4-mini-instruct as our base models, we generated a bespoke training corpus by programmatically encrypting “Human vs AI” dataset text samples with random mono-alphabetic mappings. We then applied Group-Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) fine-tuning and evaluated a novel test-time scaling mechanism designedto scale performance during inference. Our experiments measured accuracy using RapidFuzz similarity (a fuzzy similarity metric), comparing GRPO alone as well as GRPO combined with test-time scaling against initial baselines. We found that GRPO fine-tuning yielded improvements in the decryption accuracy of SLMs on this task. The test-time scaling mechanism was evaluated for its ability to reduce ambiguous substitutions, and its effect on overall performance is discussed. Our results quantify the effectiveness and highlight the limitations of these methods for lightweight cryptanalysis using SLMs, illuminating remaining failure modes and informing approaches for future research.
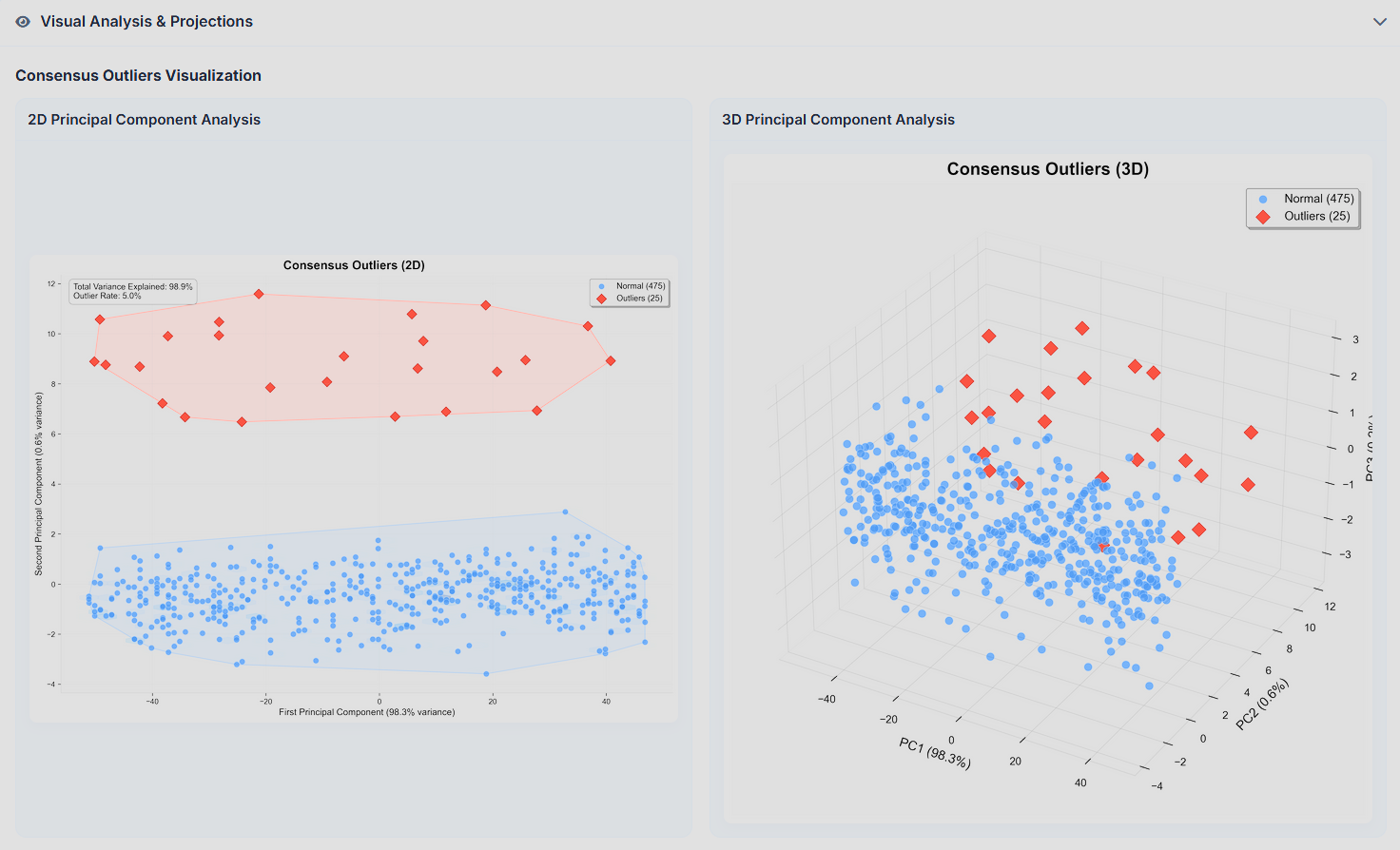
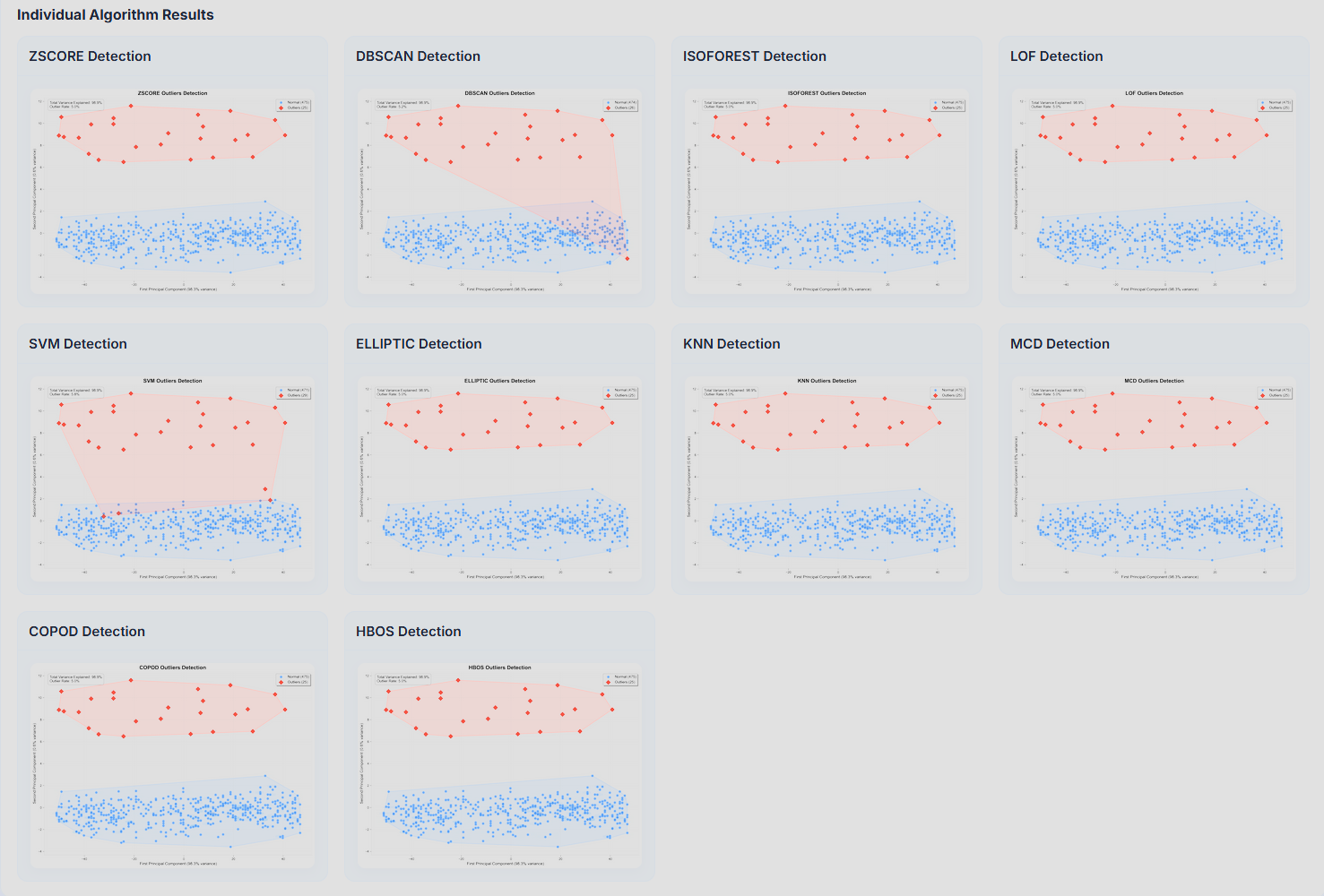
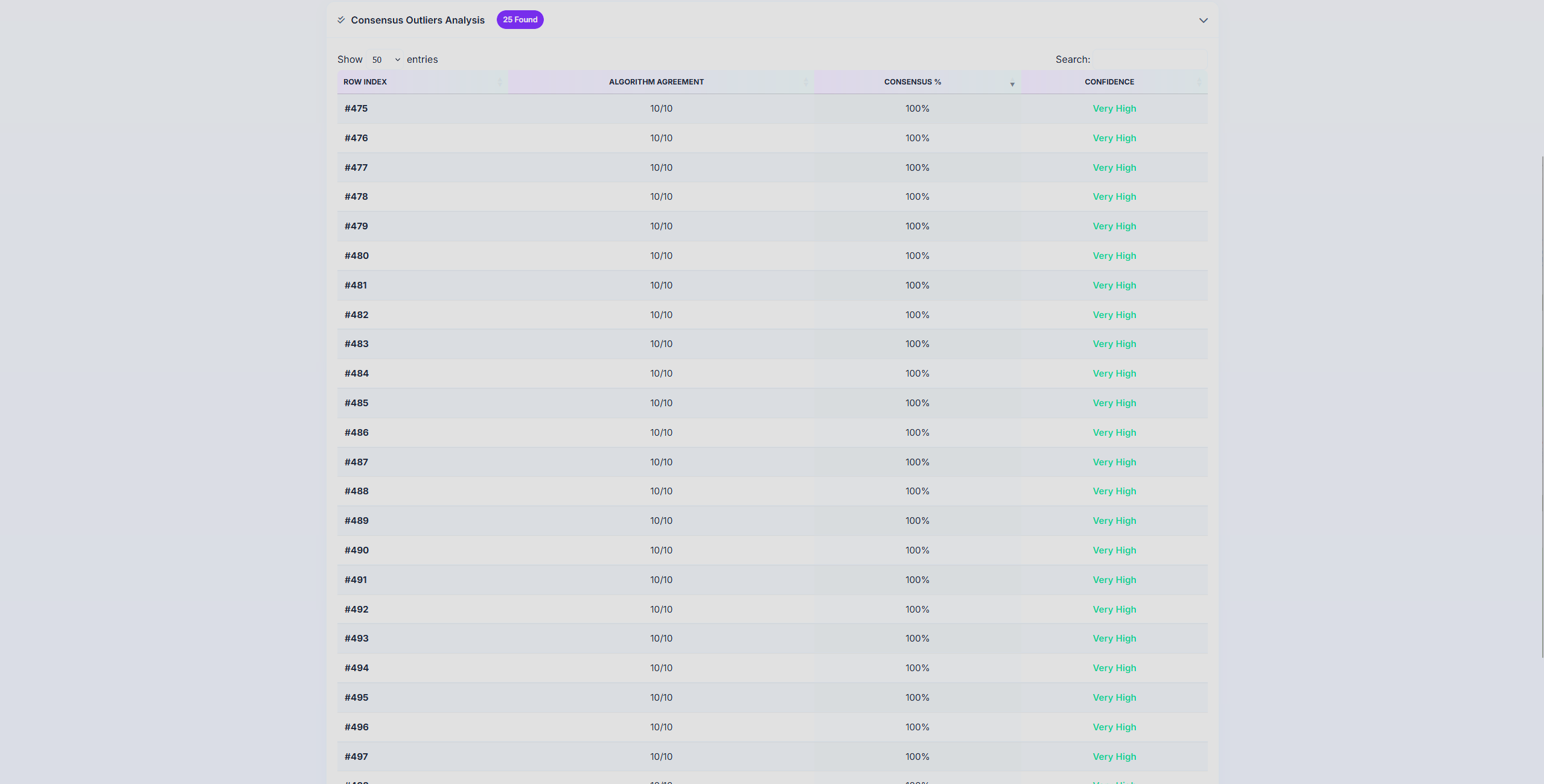
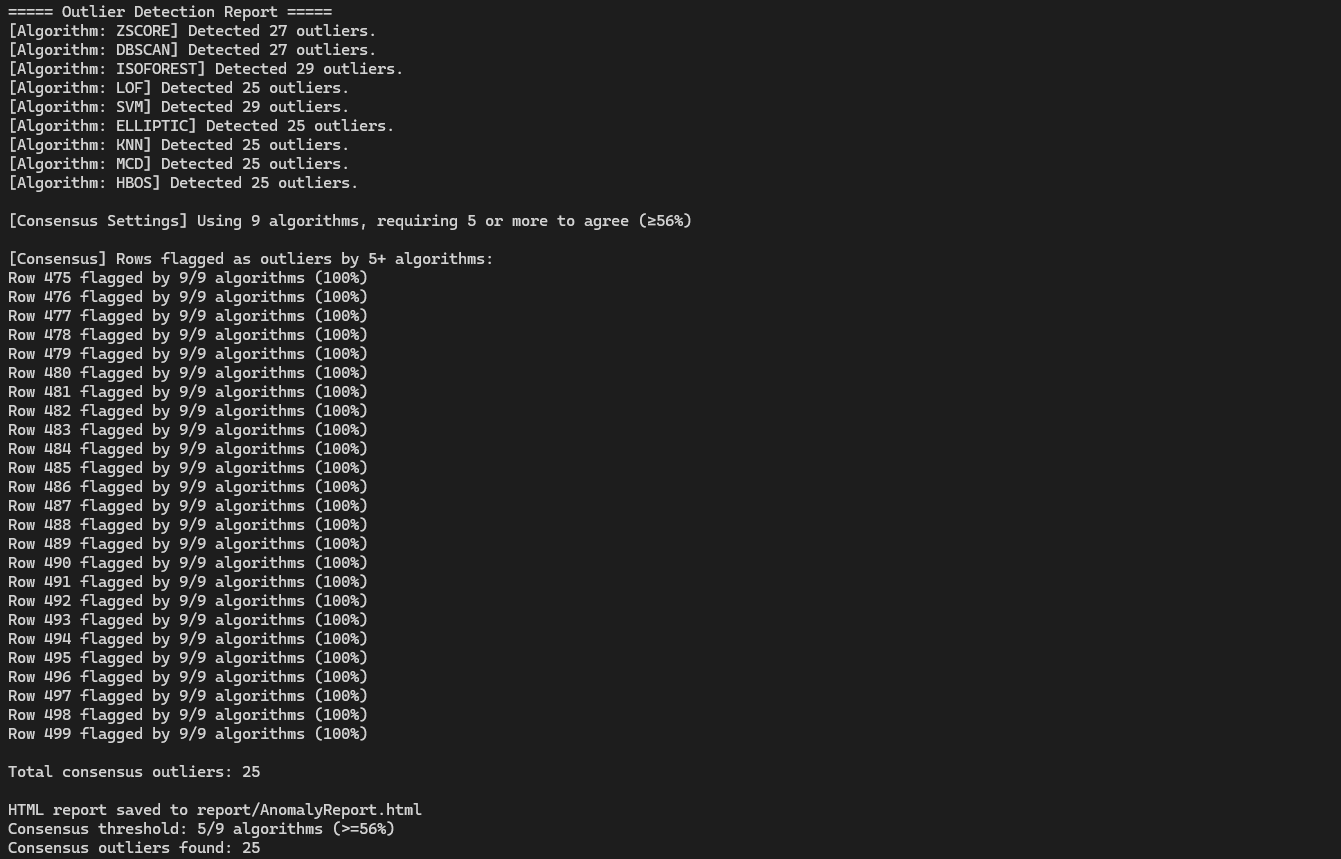
AnomalyViz
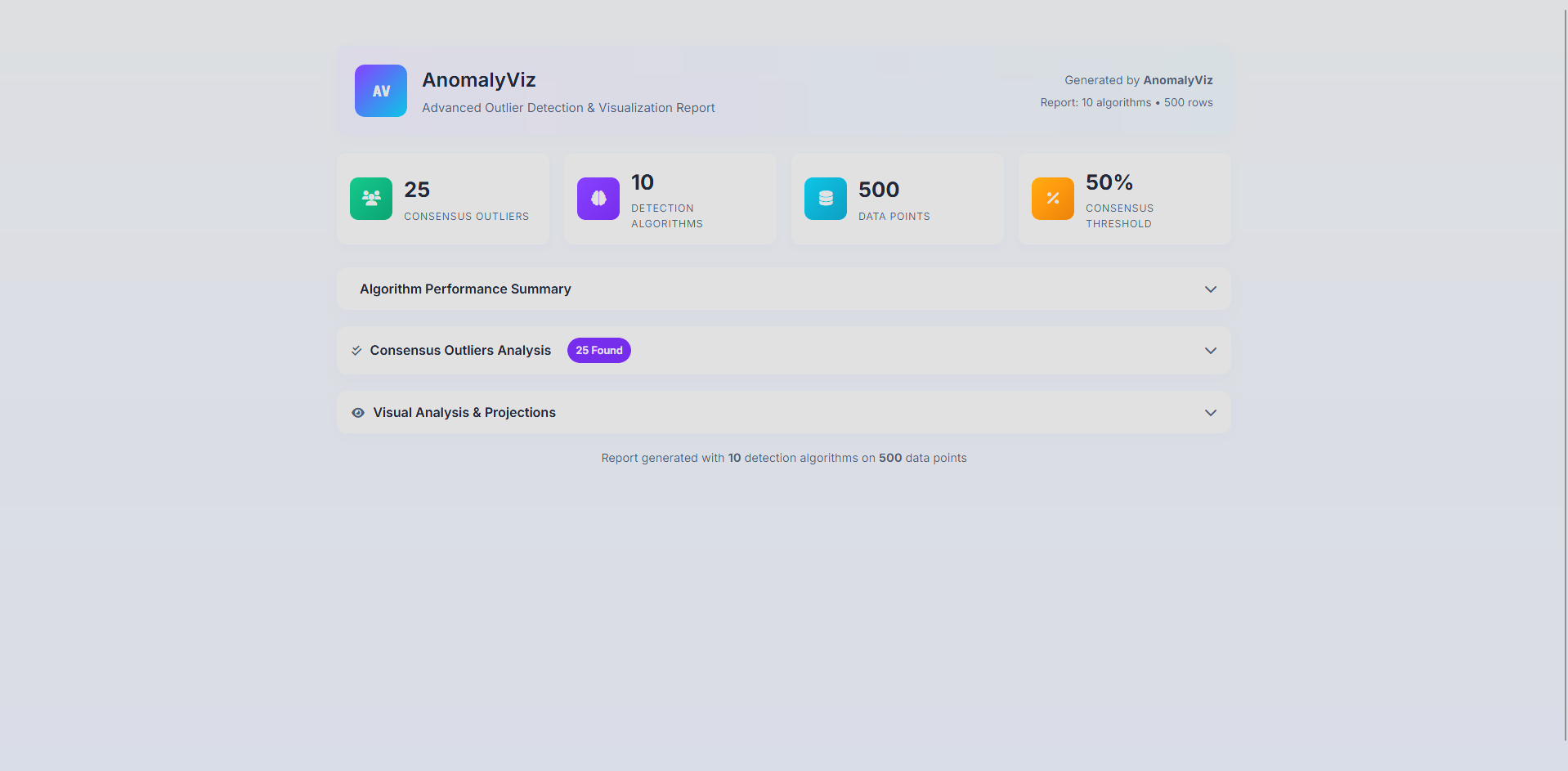
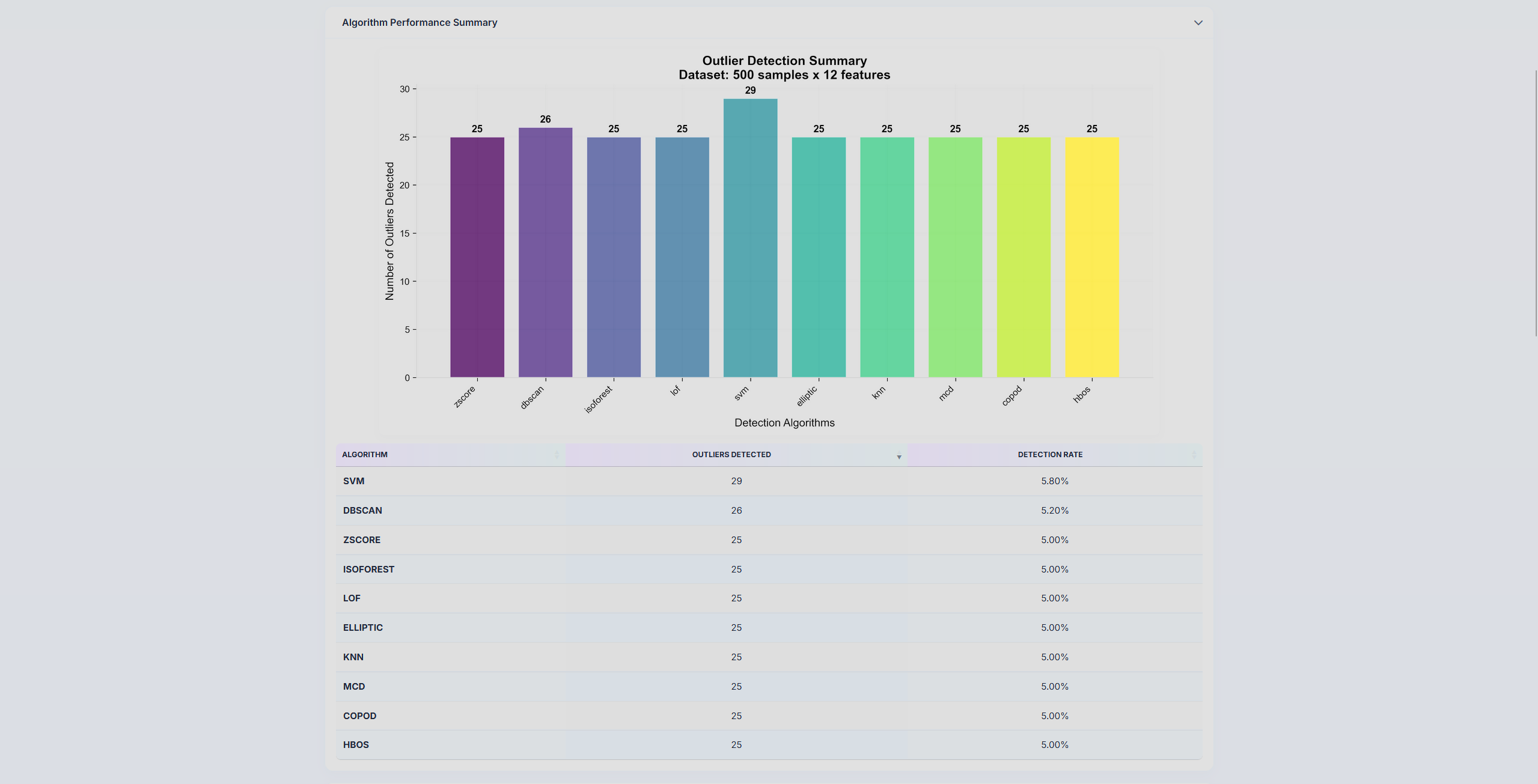
AnomalyViz is a visual outlier detection tool designed to analyze tabular data from CSV files and identify anomalies using a wide array of detection algorithms. By applying statistical (Z-Score, IQR), clustering-based (DBSCAN), machine learning (Isolation Forest, One-Class SVM, Local Outlier Factor), and dimensionality reduction (PCA) techniques, the system generates a consensus view of potential anomalies within the dataset. It outputs an interactive HTML report that includes sortable data tables, algorithm-specific visualizations, and consensus metrics to highlight which data points are consistently flagged as outliers. The project aims to simplify anomaly detection for data analysts and researchers by providing an automated, interpretable, and simple interface for exploring complex datasets. This is currently at a very early stage, and only works with relatively simple numeric datasets. The goal is to eventually have a fully functional tool that can be used to analyze any dataset, including text, image, and video and provide insights into the data.
Comparing the Performance of Machine Learning Techniques on Classifying Water as Potable
This project focused on evaluating the efficacy of classical machine learning models, such as Random Forests and Support Vector Machines (SVMs), in comparison to neural networks for predicting water potability. By optimizing hyperparameters and analyzing model performance, we uncovered key limitations in the base Random Forest model, particularly its difficulty in classifying potable water. To address this, we proposed a novel cutoff-based modification, yielding slight accuracy improvements. Additionally, we explored SVM kernel variations, with the RBF kernel demonstrating superior performance, particularly when mitigating class imbalance using SMOTE. The study provided insights into model behavior with a low amount of data, and approaches to enhance predictive accuracy in imbalanced datasets.
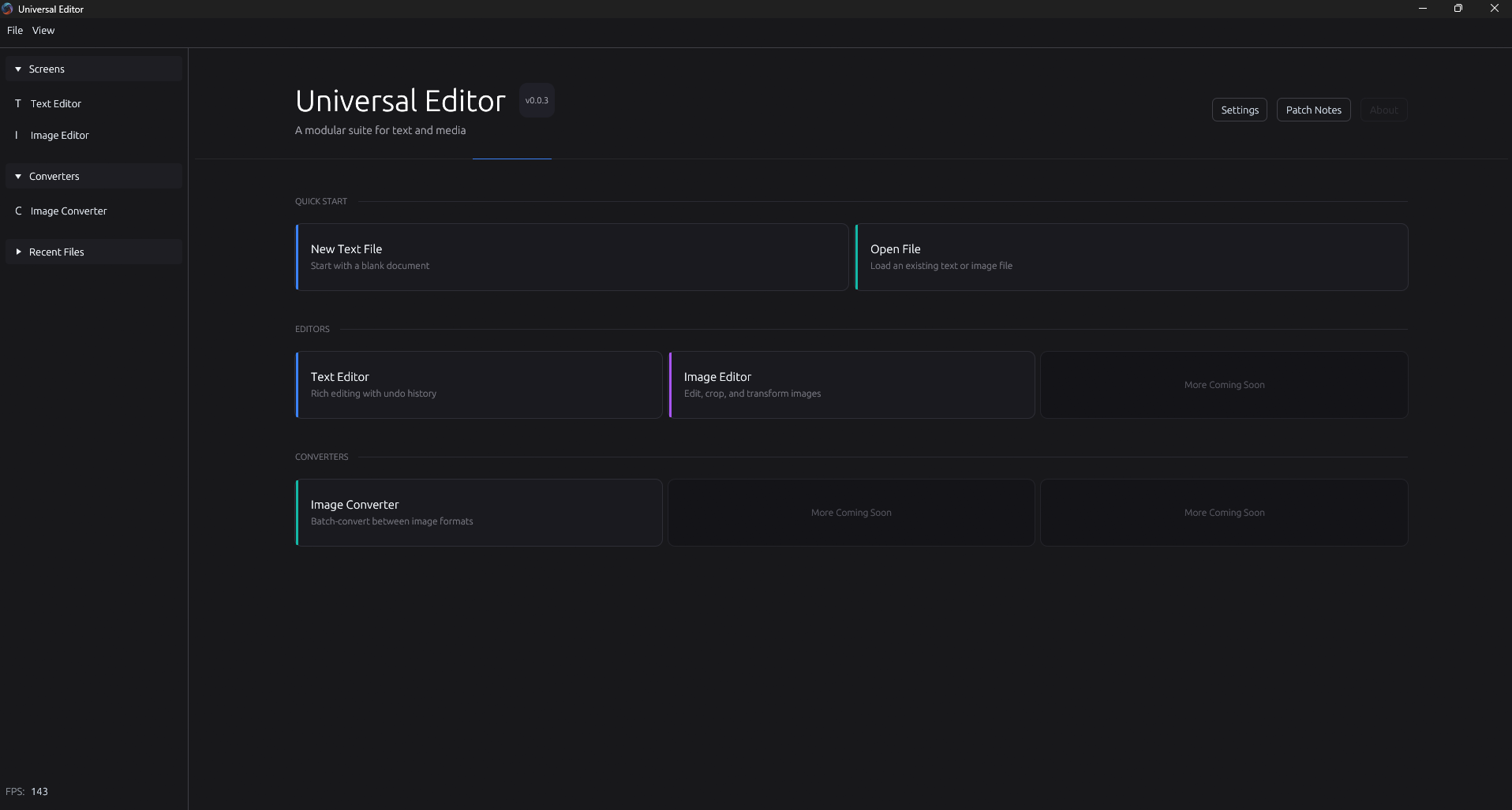
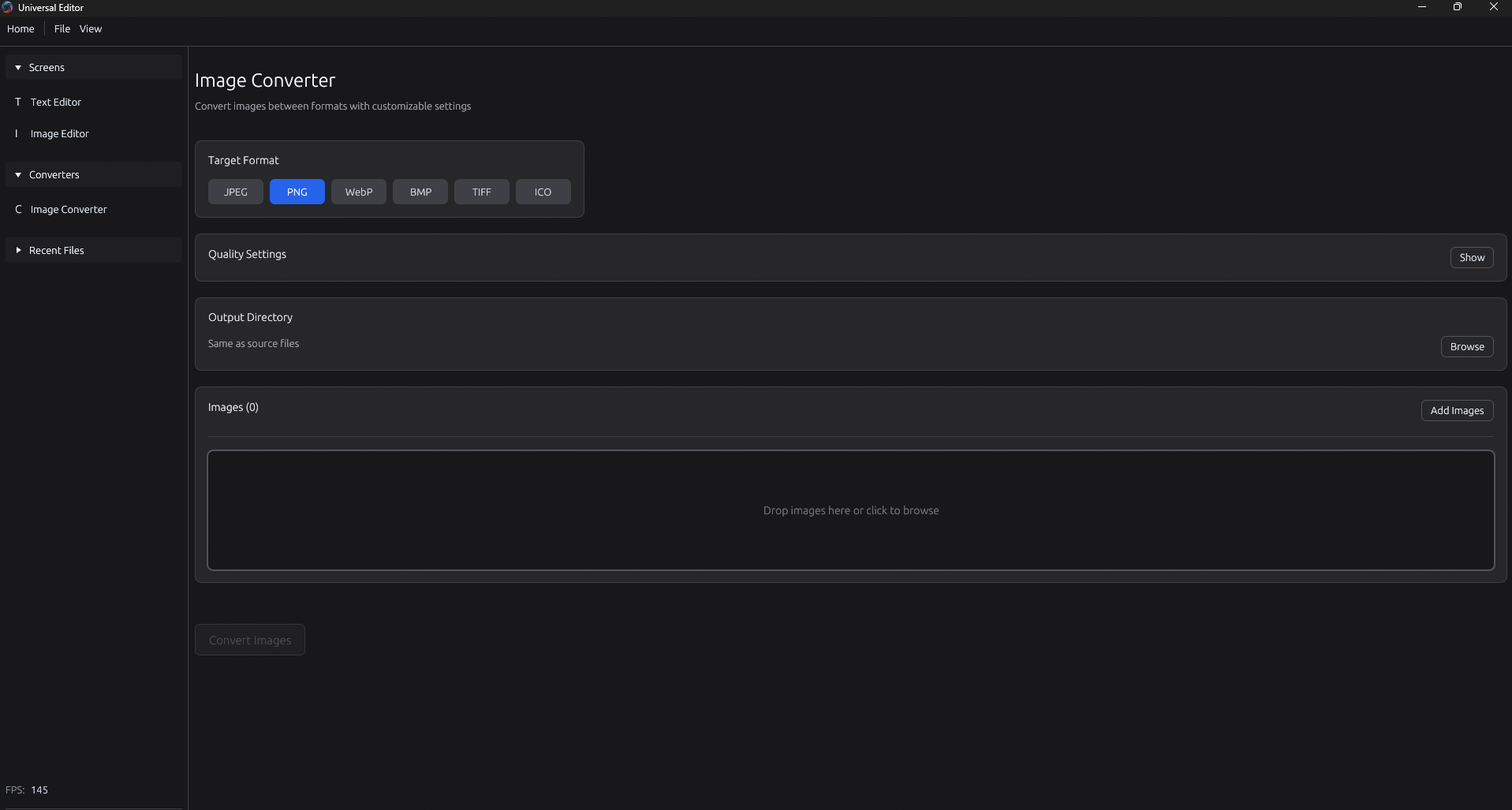
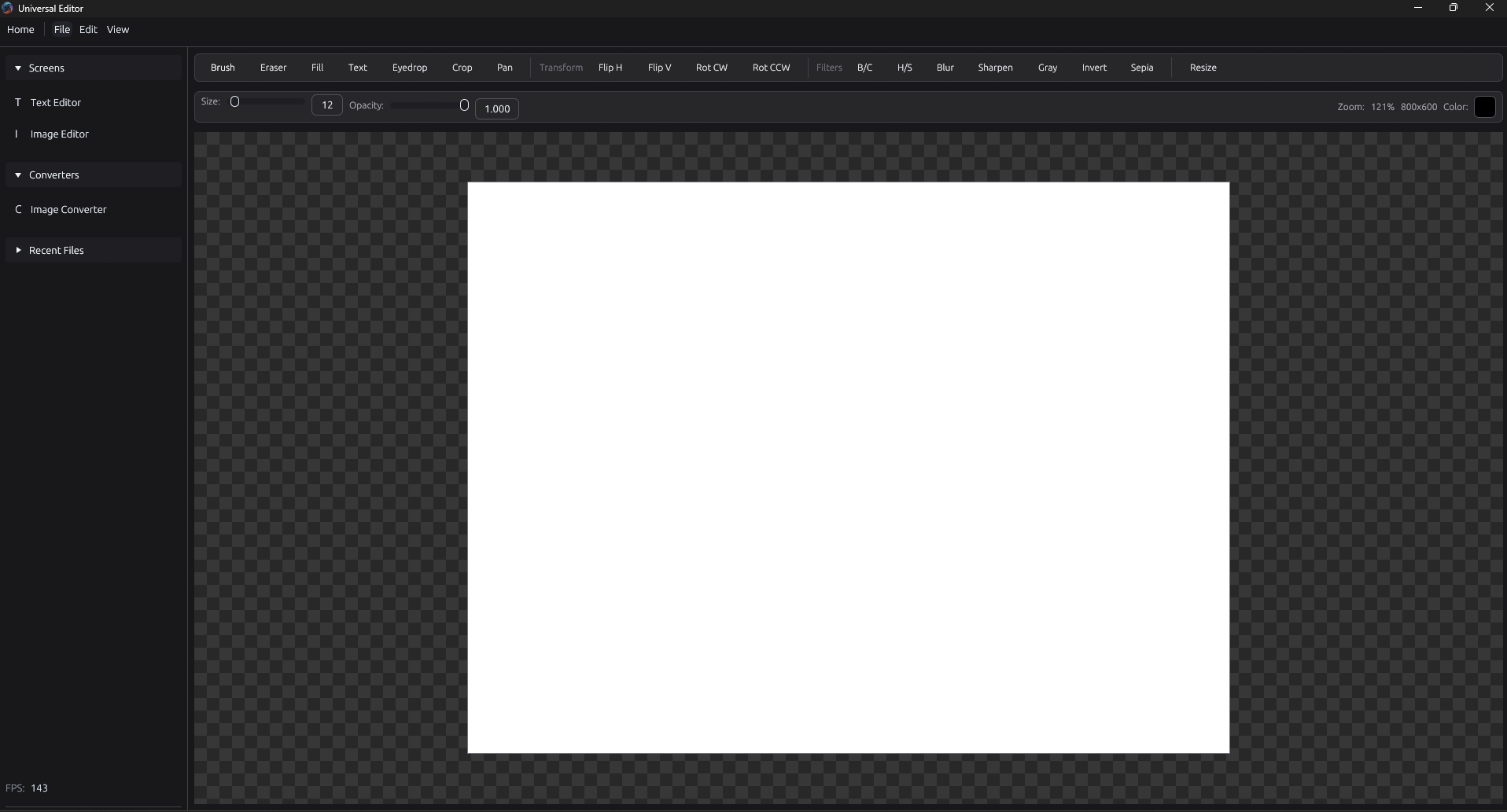
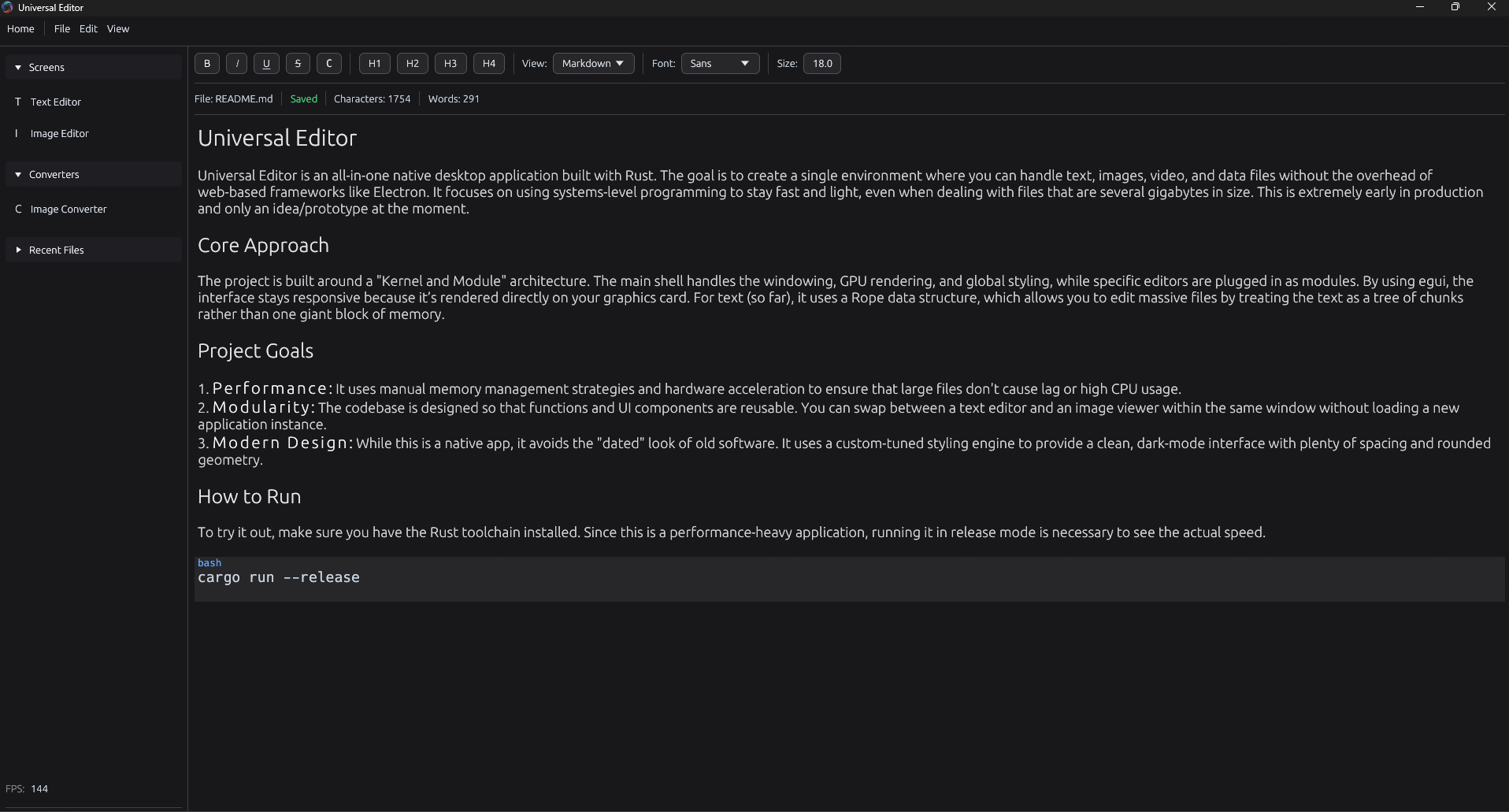
Universal Editor
Universal Editor is an all-in-one native desktop application built with Rust. The goal is to create a single environment where you can handle text, images, video, and data files without the overhead of web-based frameworks like Electron. It focuses on using systems-level programming to stay fast and light, even when dealing with files that are several gigabytes in size. This is extremely early in production and only an idea/prototype at the moment. The project is built around a "Kernel and Module" architecture. The main shell handles the windowing, GPU rendering, and global styling, while specific editors are plugged in as modules. By using egui, the interface stays responsive because it's rendered directly on your graphics card. For text (so far), it uses a Rope data structure, which allows you to edit massive files by treating the text as a tree of chunks rather than one giant block of memory. Currently, a text editor module with Markdown support, as well as a prototype image editor is available.
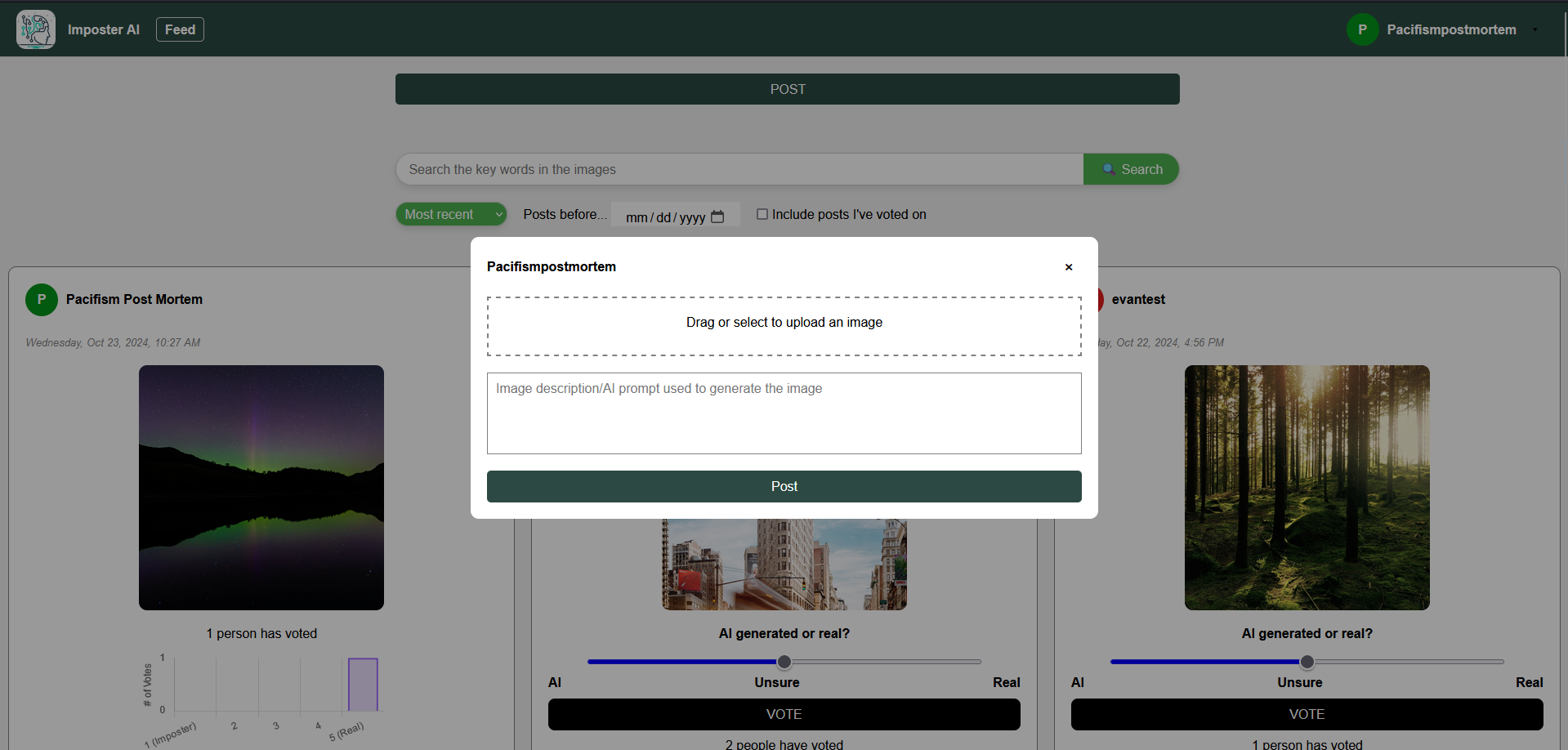
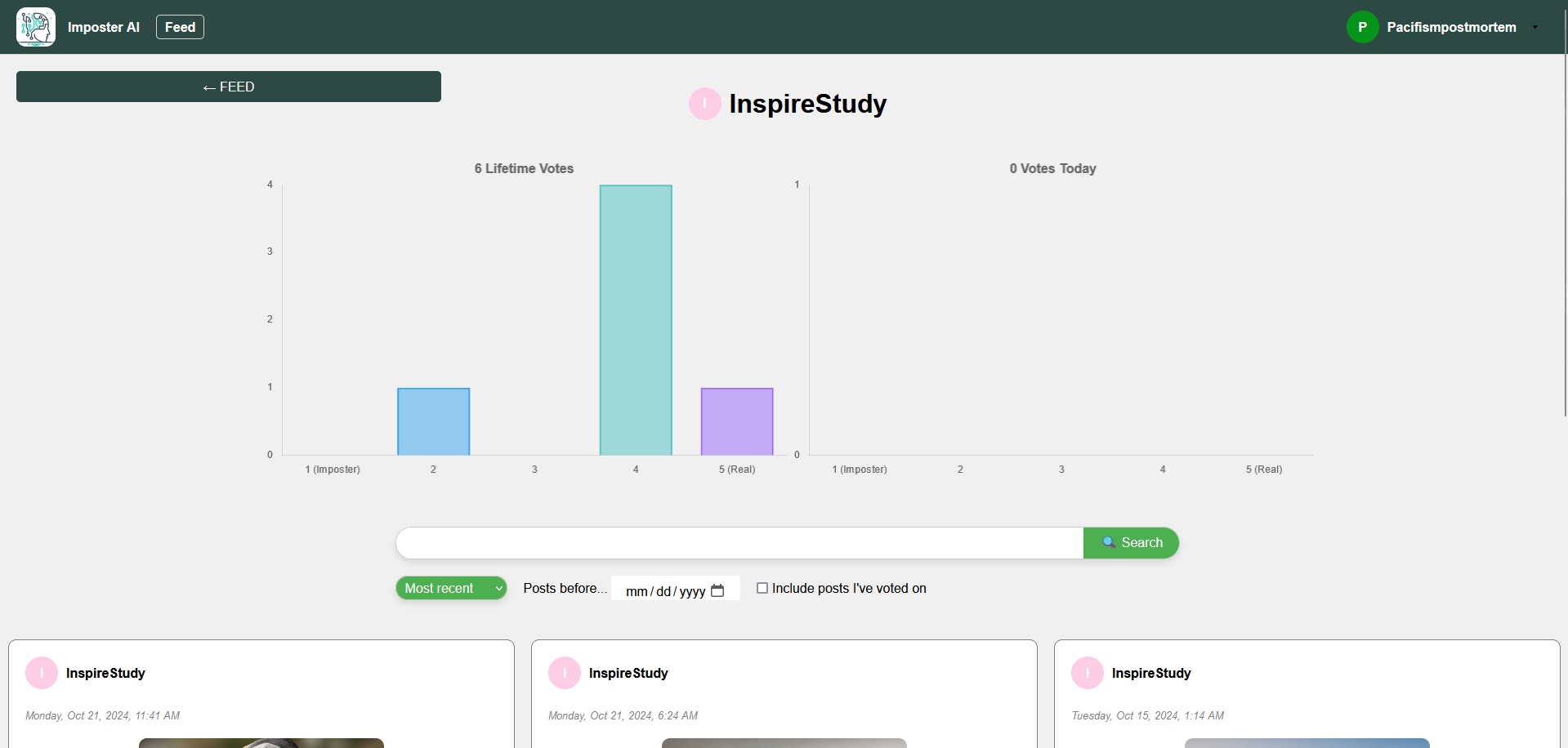
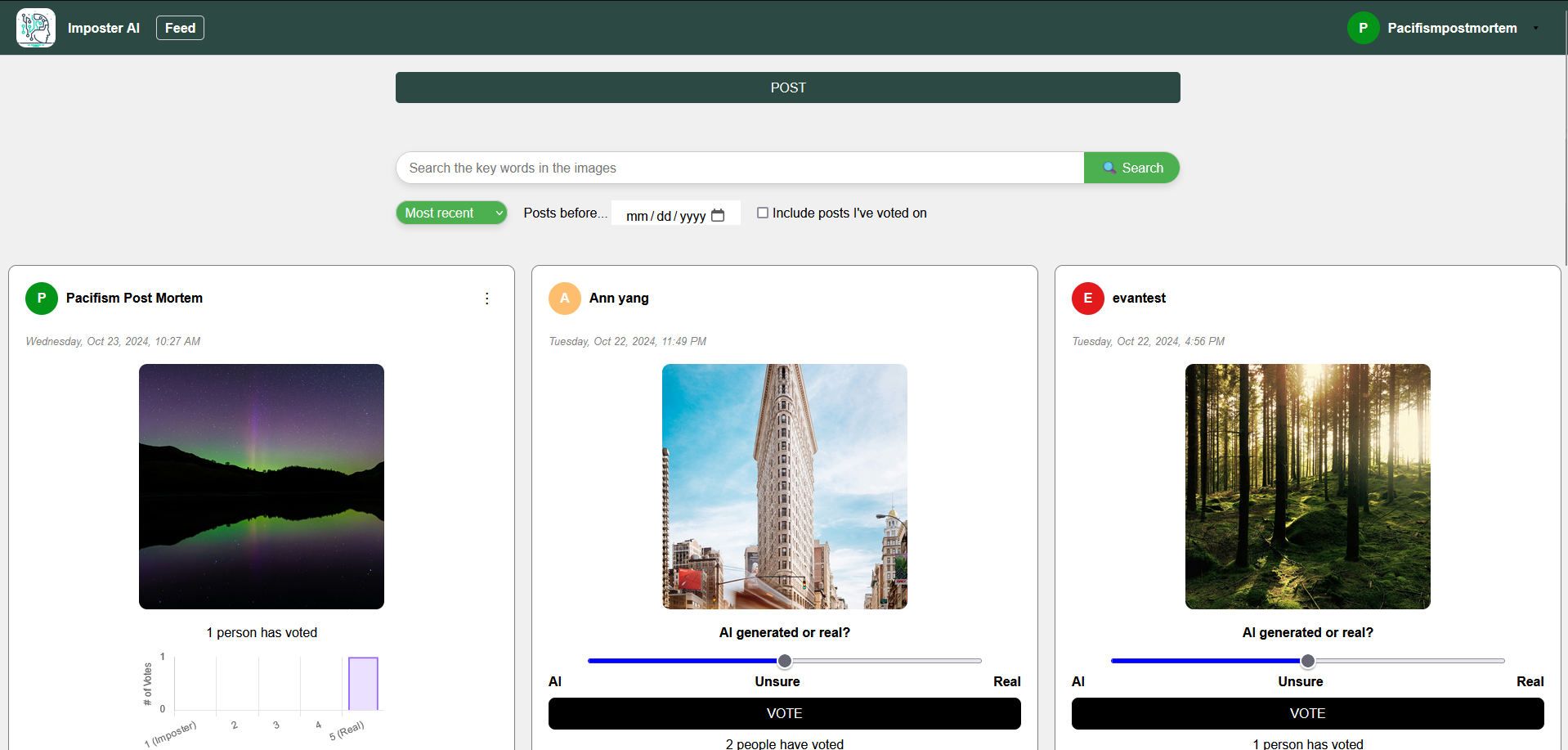
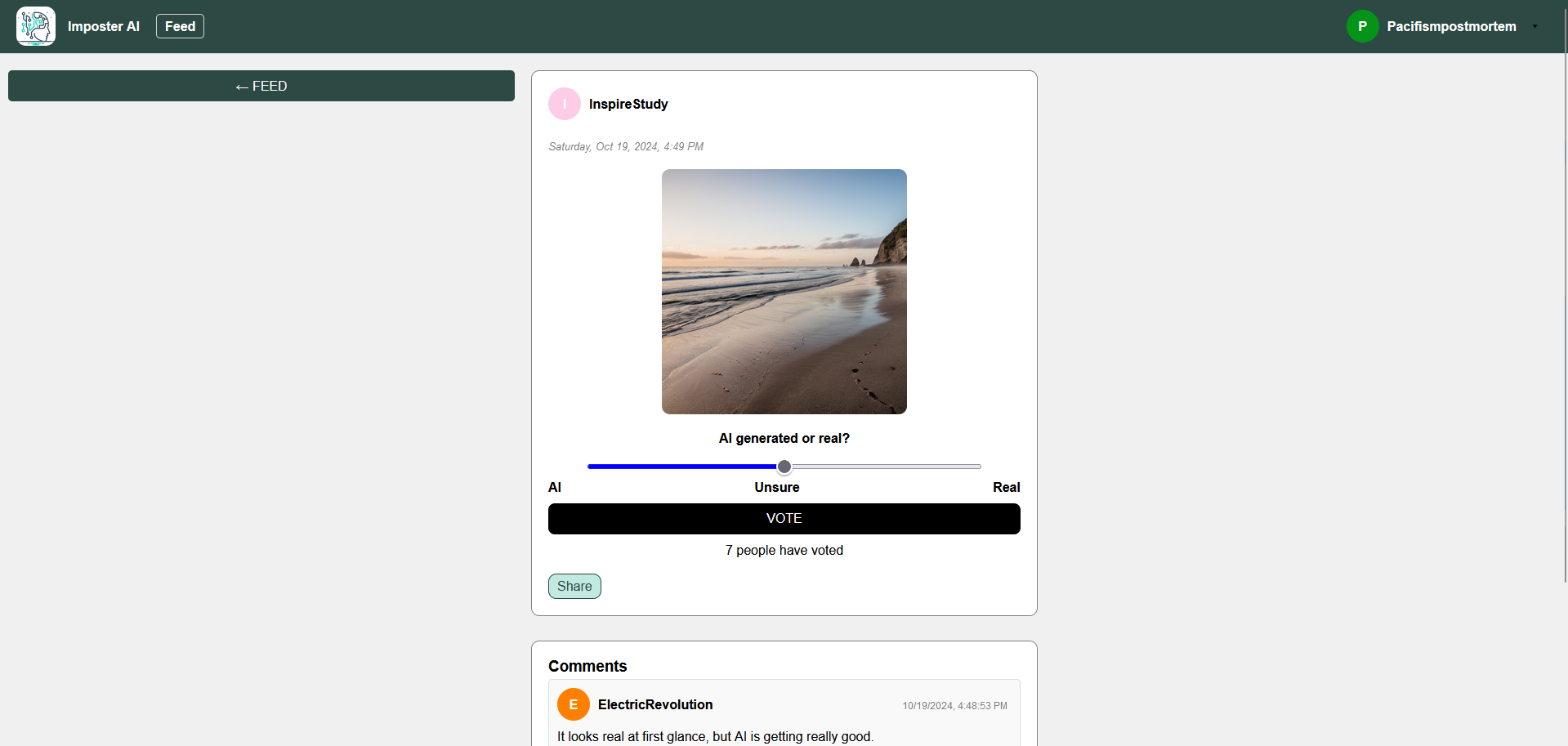
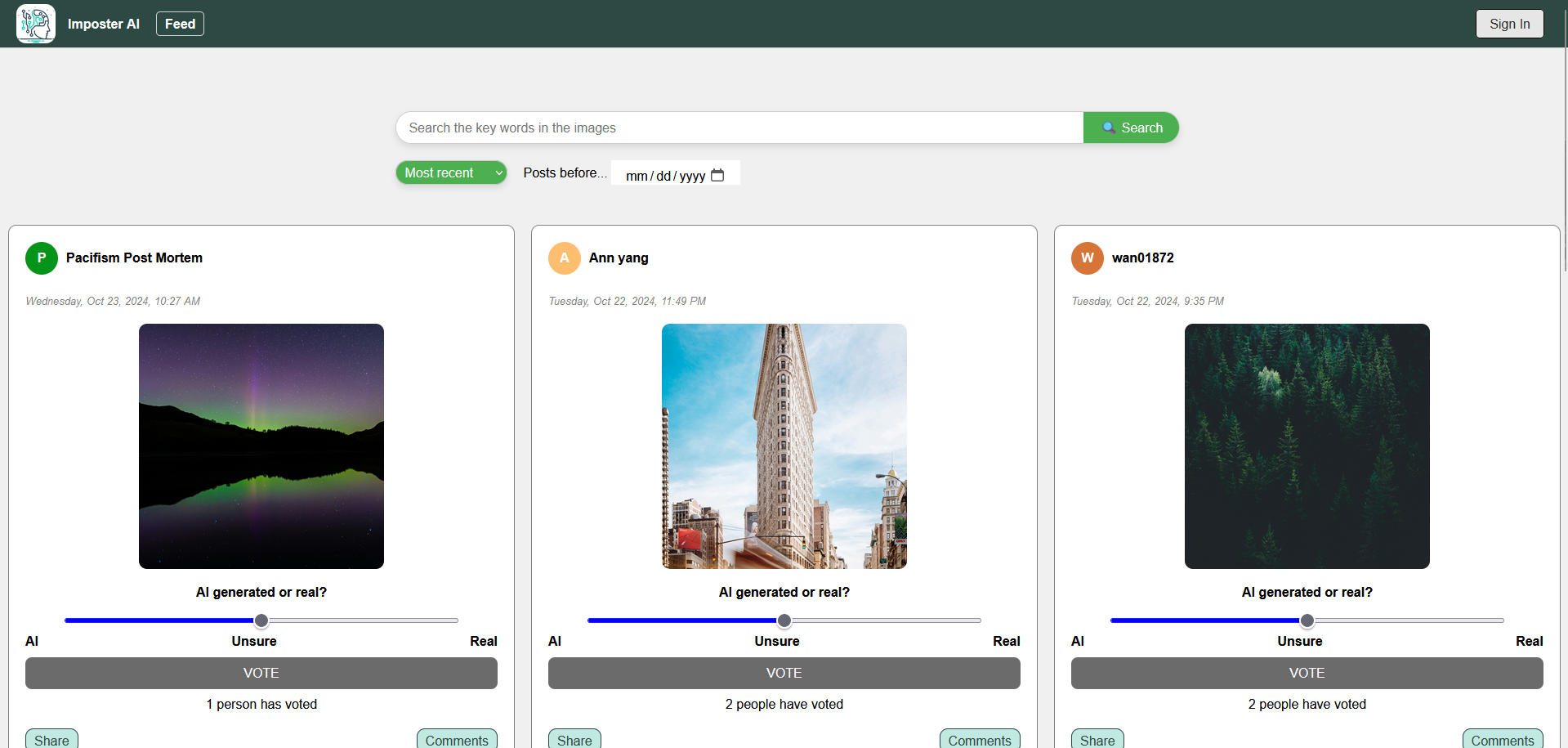
ImposterAI
ImposterAI is an interactive social media platform designed to engage users in identifying whether text, images, or videos are AI-generated or real. Users can post content and others vote on a scale from 1 (very sure it's AI) to 5 (very sure it's real), with results displayed in an aggregate graph after voting. The platform encourages interaction through comments, sharing features, and personalized profiles where users can view their posting and voting statistics. Key technical highlights include dynamic post loading with JavaScript's fetch and AbortController for a seamless user experience, a responsive design optimized for mobile and desktop, efficient image storage using Azure Blob Storage, and advanced search, sort, and filter options to enhance content discovery. ImposterAI offers both a fun way to test AI detection skills and a practical tool for assessing the authenticity of digital content.
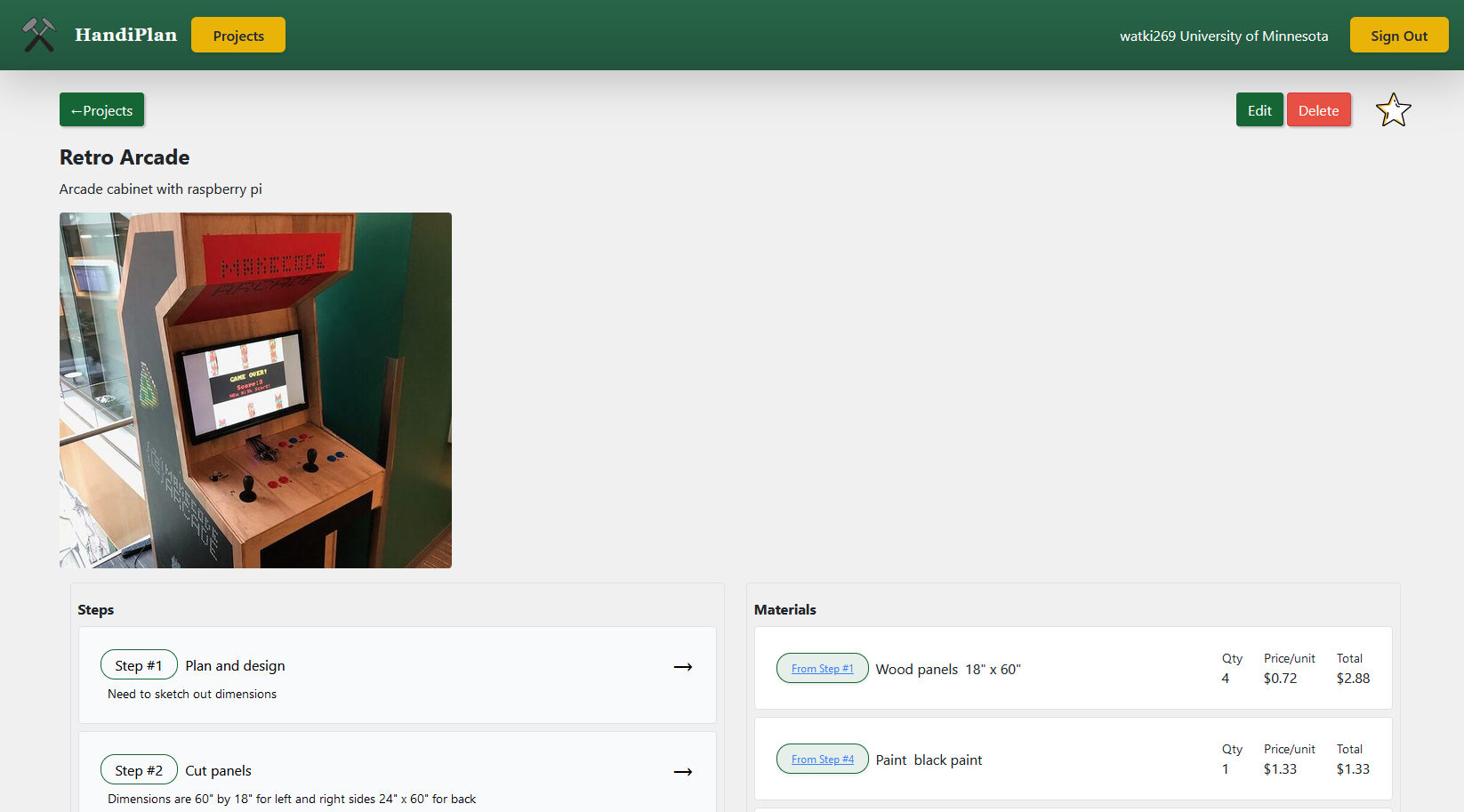
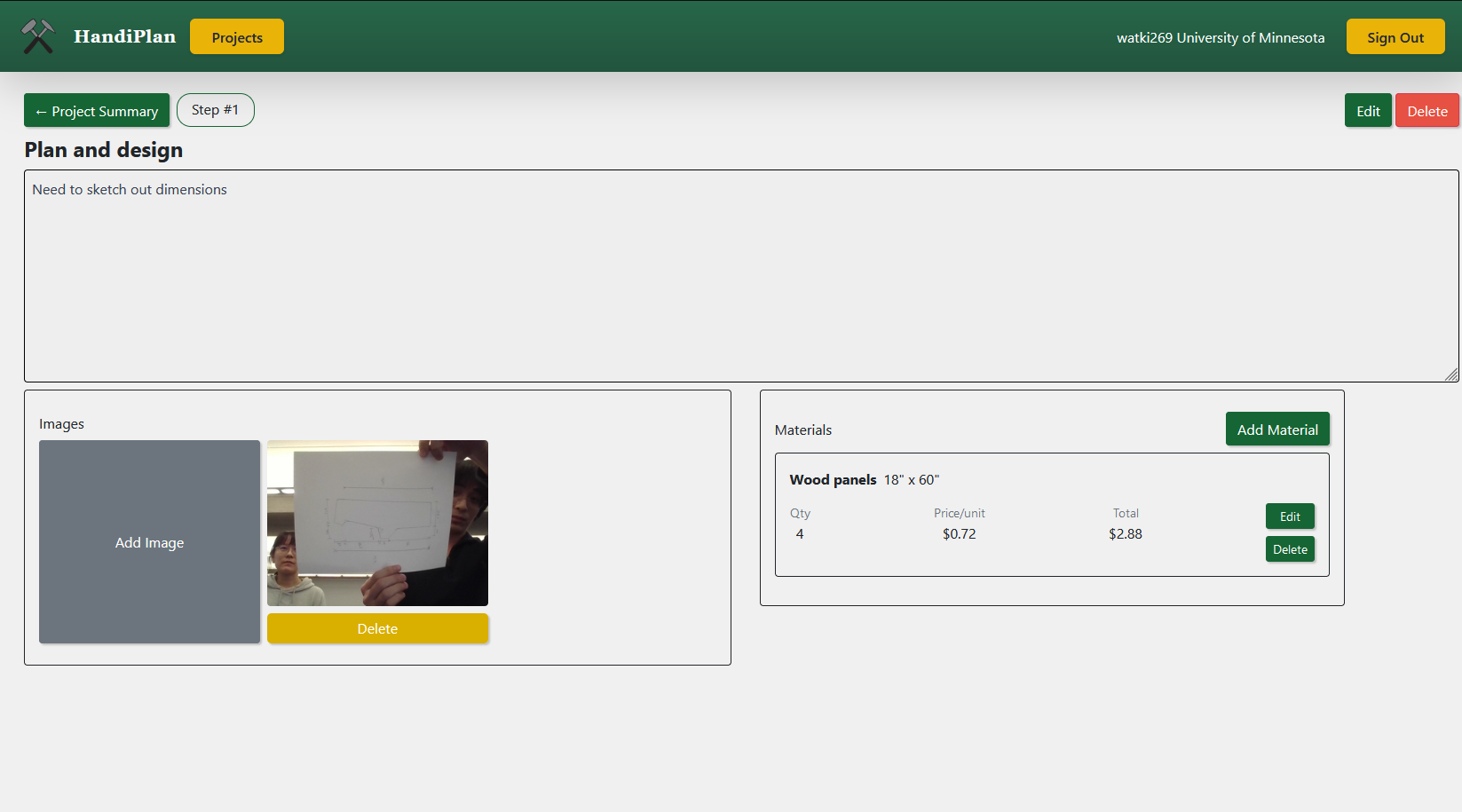
Handiplan
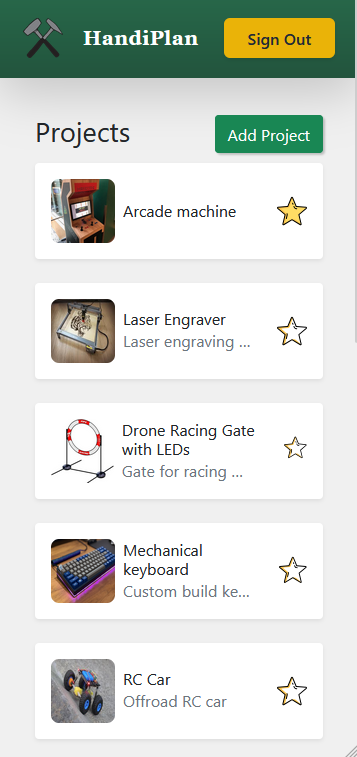
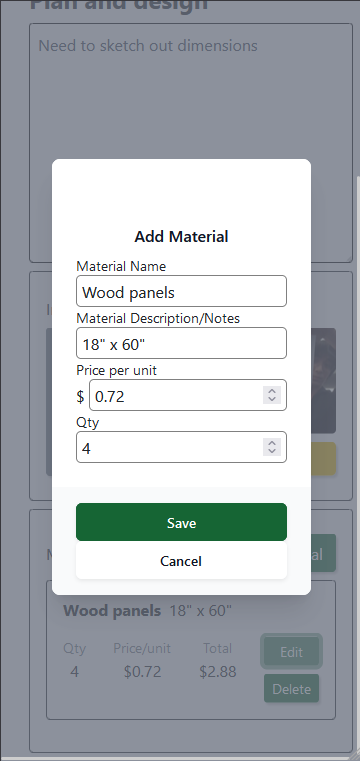
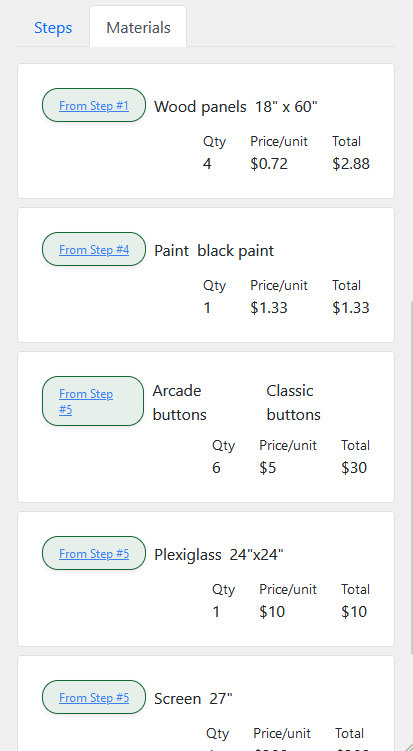
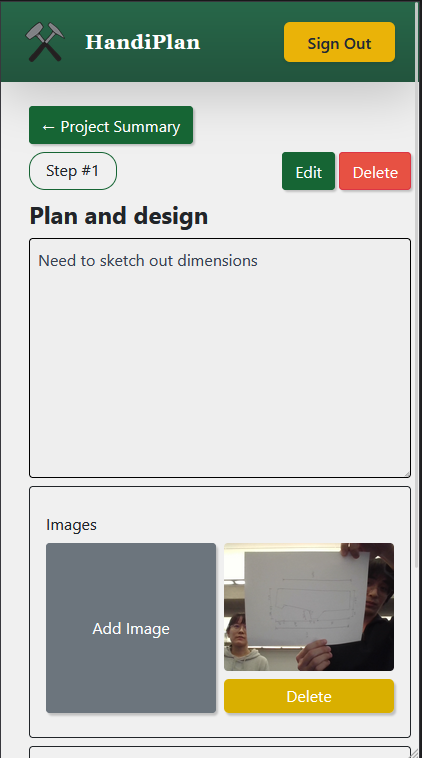
Handiplan is an intuitive project tracker designed for woodworking, DIY, and hands-on enthusiasts to streamline project organization and recreation. It allows users to create detailed project plans with steps, notes, and material lists, complete with cost tracking. Users can capture and upload images directly via integrated camera functionality, ensuring every design and progress detail is recorded. With a mobile-friendly interface and installable PWA support, Handiplan makes it easy to access project details anywhere, whether you're in the workshop or at the store. The app's robust backend, built with Firebase, ensures seamless state management and secure data storage for all creative endeavors.
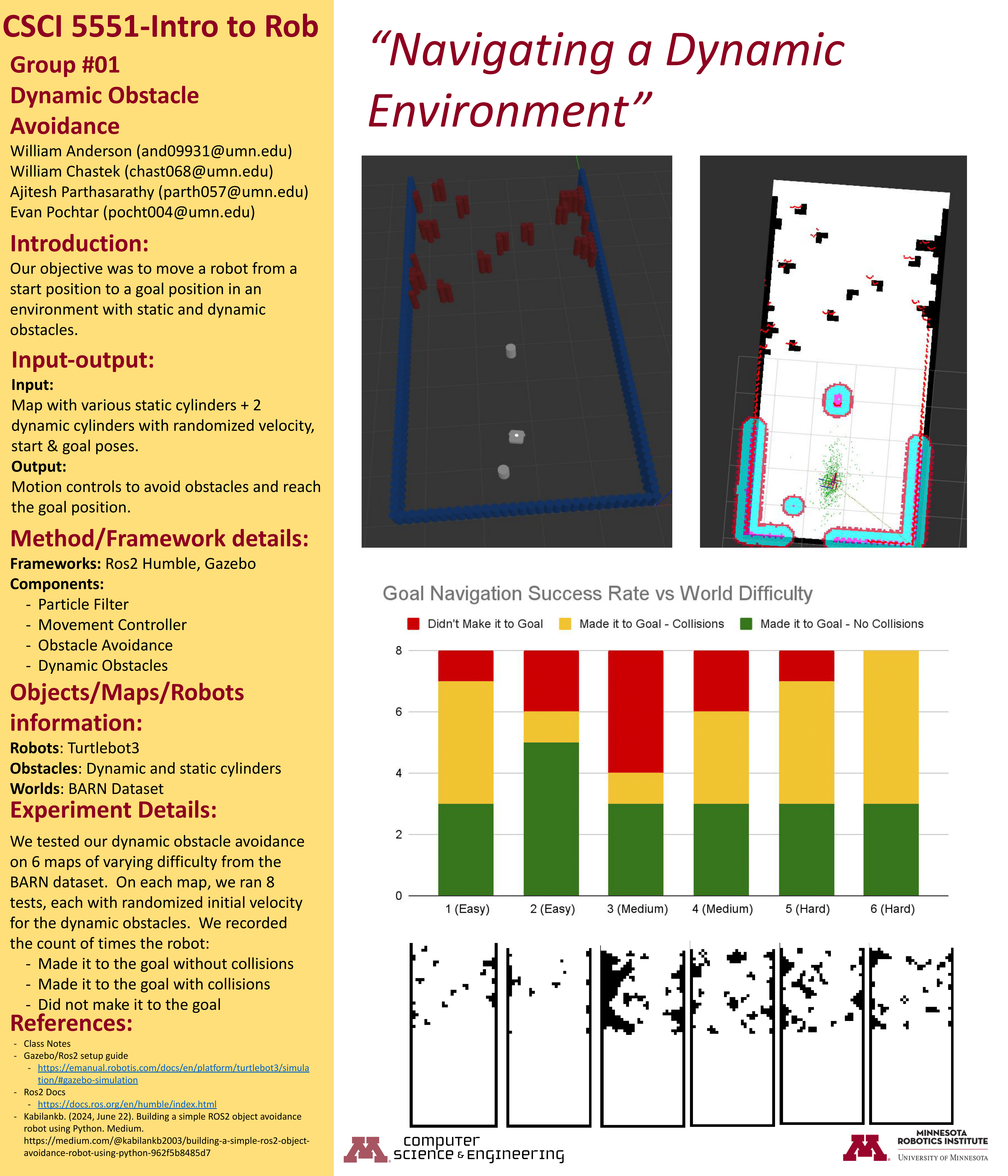
Navigating a Dynamic Environment with LiDAR using a Turtlebot3 Robot
This project addresses the challenge of autonomous navigation in environments containing both static and dynamic obstacles. The objective was to guide a Turtlebot3 robot from a predefined start position to a goal location within simulated environments featuring cylindrical obstacles—both stationary and dynamically moving with randomized velocities. The system takes as input a map containing these obstacles along with the robot's start and goal poses and outputs motion controls that enable the robot to reach the goal while avoiding collisions using only 5 LiDAR scans per second. Implemented using ROS2 Humble and the Gazebo simulator, the system integrates key components including a particle filter for localization, a movement controller, and an obstacle avoidance module with dynamic obstacle handling. Evaluation was conducted using six maps of varying complexity from the BARN (Benchmark of Autonomous Robot Navigation) dataset, with eight randomized trials per map. Outcomes were recorded in terms of successful, partially successful (with collisions), and failed attempts to reach the goal, demonstrating the system's performance under different levels of environmental difficulty.
Nation-State Database
A high-performance interactive world map built with SvelteKit, D3.js, and Svelte 5. Click any country to explore detailed information including demographics, economics, and history, all rendered client-side with smooth animations and data visualizations. This project serves as a comprehensive nation information platform that combines geographic visualization with clean visuals. Unlike database/server-driven applications, it operates entirely through static assets and client-side processing, making it fast and easily deployable. The interface is mainly a fullscreen interactive map that responds to user interaction with D3-powered zoom animations, while a resizable information panel presents country data including economic indicators with historical charts, political summaries, and detailed historical timelines. The application manages data fetching from multiple sources while maintaining local caches to minimize API calls and speed up response times. Data can be optionally persisted to static JSON files (all of which is located within the repo), creating a self-improving dataset that grows more complete with each use. Multiple visualization modes include traditional geographic themes and chloropleth maps that color countries by economic metrics like GDP or income inequality, with interactive legends and tooltips.
JSON Studio

A modern JSON editor built with SvelteKit that makes editing complex JSON files easy and efficient for both developers and non-technical users. Currently this is an experimental tool for exploring editing workflows and user interfaces, not a finished or production-ready product. This is a work-in-progress with known limitations. The app provides three view modes: a Tree view with expandable nodes and inline editing, a Table view for a spreadsheet-like representation with sortable columns, and a Text view that shows raw JSON with formatting, basic validation, line numbers, and simple editing helpers. There is a global search with optional key-scoped filtering, the ability to focus on a sub-object or array, a 50-level undo/redo stack, and a simple auto-save behavior. The application is optimized for handling large JSON files through indexed search capabilities that deliver sub-100ms response times and memory-efficient rendering systems. The interface remains responsive even when working with datasets containing thousands of nodes, making it suitable for complex API responses, configuration files, and structured content management.
Framiax
Framiax is a desktop application designed for adding rich annotations to videos without relying on the cloud or online accounts. It lets you load a video file, pause or scrub to any point, and attach notes or drawings directly to specific time stamps. Annotations can be simple text comments or freehand sketches over the video frame. Multiple people can review and contribute to the same video session in real time on a shared screen, making it useful for team feedback, training reviews, creative collaboration, or detailed analysis. When you're done, you can export the annotated video for archiving or later playback, with all notes and drawings preserved. Everything runs locally on your machine. There is no login, no online storage, and no background services. Your files and annotations stay under your control. This project is in a very early stage and still in concurrent development.
ExetrixAnalysis
A cross-language performance analysis tool built in Rust. This utility executes a program written in any common language and collects detailed runtime statistics. It reports per-function execution times, memory allocation trends, and peak resource usage. Designed for experimenters and developers who want insight into where their code spends the most time, it generates both structured JSON output for further analysis and a styled interactive HTML report for immediate visualization. The tool runs locally, making it private, easy to use, and fully customizable. This project is currently only a proof of concept, and is not yet fully functional.
Evan-Pochtar.github.io
This is the website you are currently viewing! It was created for the purpose to show more of the projects and papers I have worked on, as well as expanding upon me as a person. Some of the papers especially, I felt were really important to me and my learning, that couldn't be relayed on a few bullet points in a resume. This website will be frequently maintained and updated with relevenat information. This was created purely in HTML and CSS, without any form of framework for the frontend. The website was designed to be both desktop and mobile friendly, fitting any screen size.
A Comparative Study of Maze Solving and Maze Creation Algorithms
Developed a Python application to evaluate and compare the performance of various search algorithms in solving procedurally generated mazes. The tool generates customizable mazes of varying dimensions and solves them using algorithms such as BFS, DFS, A*, Best-First Search, Simulated Annealing, and Genetic Algorithms. Performance metrics—runtime, nodes searched, and path length—were tracked and analyzed to rank the algorithms individually and overall. The system visualizes results through detailed graphs, providing insights into the efficiency and suitability of each algorithm for specific problem scales. Custom maze generation and algorithm implementations ensured flexibility and reliability in testing.
StudyBuddy: Minnehack 2023

Study Buddy is a web platform created during the MinneHack2023 Hackathon (January 28-29, 2023) to bridge the gap between students and volunteer tutors in their community. The platform connects learners with tutors who not only excel in specific subjects but also share similar interests, fostering a personalized learning experience. Key features include a live chat system powered by WebSockets for real-time interaction and an OpenAI API integration for automated responses when a tutor is unavailable. Built with Django for the backend and React for the frontend, Study Buddy utilizes a REST API for seamless communication and incorporates a sophisticated ranking algorithm to match students and tutors effectively. The project highlights the importance of education as both a personal and civic good, emphasizing community participation to uplift learning opportunities. Accomplishments include generating realistic test data, mastering new technologies like Django and modern React, and iteratively refining the platform's design.
SPORTS: A Sports Scheduling System
The SPORTS system, built using Python and Pandas, is a robust platform designed to streamline the management of recreational sports leagues. It enables efficient scheduling of games, venue bookings, and team registrations by processing CSV data files to generate accurate and conflict-free schedules. The system supports multiple sports, venues, and league types while accommodating regional regulations, weather constraints, and concession policies. With a focus on reliability, scalability, and ease of use, SPORTS provides secure access for league administrators, team managers, and other stakeholders, ensuring smooth operations and compliance with league-specific requirements. This was created in an Agile-Scrum framework, however the assignments worked in more of a Waterfall approach. The strength of this project was creating both detailed requirements and designs for the project at hand, and being able to recognize when those design decisions need to change based on the current needs of the stakeholders and program itself.
Proddash
ProdDash is a productivity dashboard designed to transform the browser's new tab page into a centralized area for managing daily tasks and streamlining everyday activities. The platform currently features a daily to-do list, a search bar, date display, and encrypted user authentication, with a clean and functional interface. The project has expanded to include a variety of features such as customizable quick links, task scheduling options that adapt to user preferences, and integrations with popular tools like Google and Outlook calendars. Future developments include a Chrome extension for seamless replacement of the new tab page, and a centeralized server to host the webpage itself. ProdDash also aims to become a productivity tool by incorporating features like weather updates, news summaries powered by AI, calorie and workout tracking, and notecards for quick reminders. This project seeks to create a highly customizable experience where users can adjust settings, enable or disable modules, and personalize the interface with options like dark mode, background images, and tailored quick links. This website is currently not public as it is actively being worked on, this is also the reason the GitHub is not public, although this will be released as open source software afterwards.
SimpleML
These files are a compilation of classical machine learning algorithms created to work for any kind of integer inputs. This was created as a way of conceptualizing and putting to life the mathmatical formulas in class, so it would be easier to understand and work with. Although the functions are relatively simple and lacks a lot of the speedups other modules bring, it still runs relatively fast as the code does not have much bloat. In the future, speedups with systems like CUDA, PyTorch, Tensorflow, or Scikit-Learn could help with the computation even more.
Research Paper Tracker
This website is a research paper tracking application that allows users to organize and manage their academic readings. It features a clean, modern interface where users can add papers either manually or by parsing citations, include detailed metadata such as title, authors, publication information, and personal reading notes. The system supports categorizing papers by reading status (to-read, currently reading, completed, or reference), adding custom tags for easy organization, and includes a search functionality to quickly find specific papers by title, author, or tags. All data is stored locally in a JSON file managed by a Flask backend. This tool serves as an efficient digital library for researchers, students, and academics to maintain their literature reviews and research materials in one centralized location. This is one part of a future all in one tracking application that is in progress, and will eventually be written in Svelte.
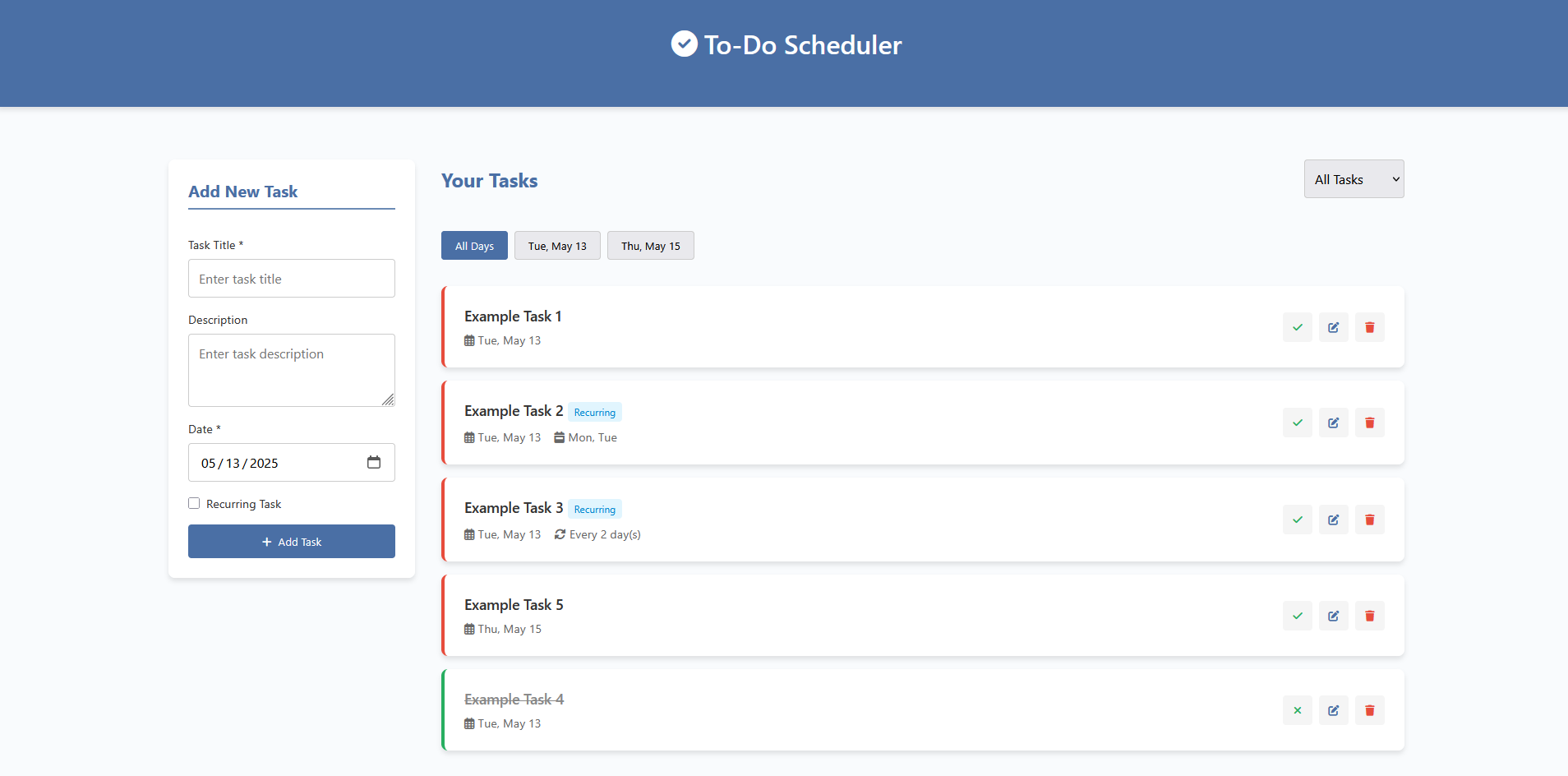
To-Do List Scheduler
This scheduler application is a task management solution designed to help people efficiently organize their daily responsibilities through a simple web interface. The application enables users to create, edit, and delete tasks, assign them to specific days, mark them as complete, and set up recurring tasks that repeat either on selected weekdays or at custom day intervals. All data is stored locally in a JSON file managed by a Flask backend. The interface also works with any different screen sizes, making it accessible on both desktop and mobile devices. This is one part of a future all in one tracking application that is in progress, and will eventually be written in Svelte.
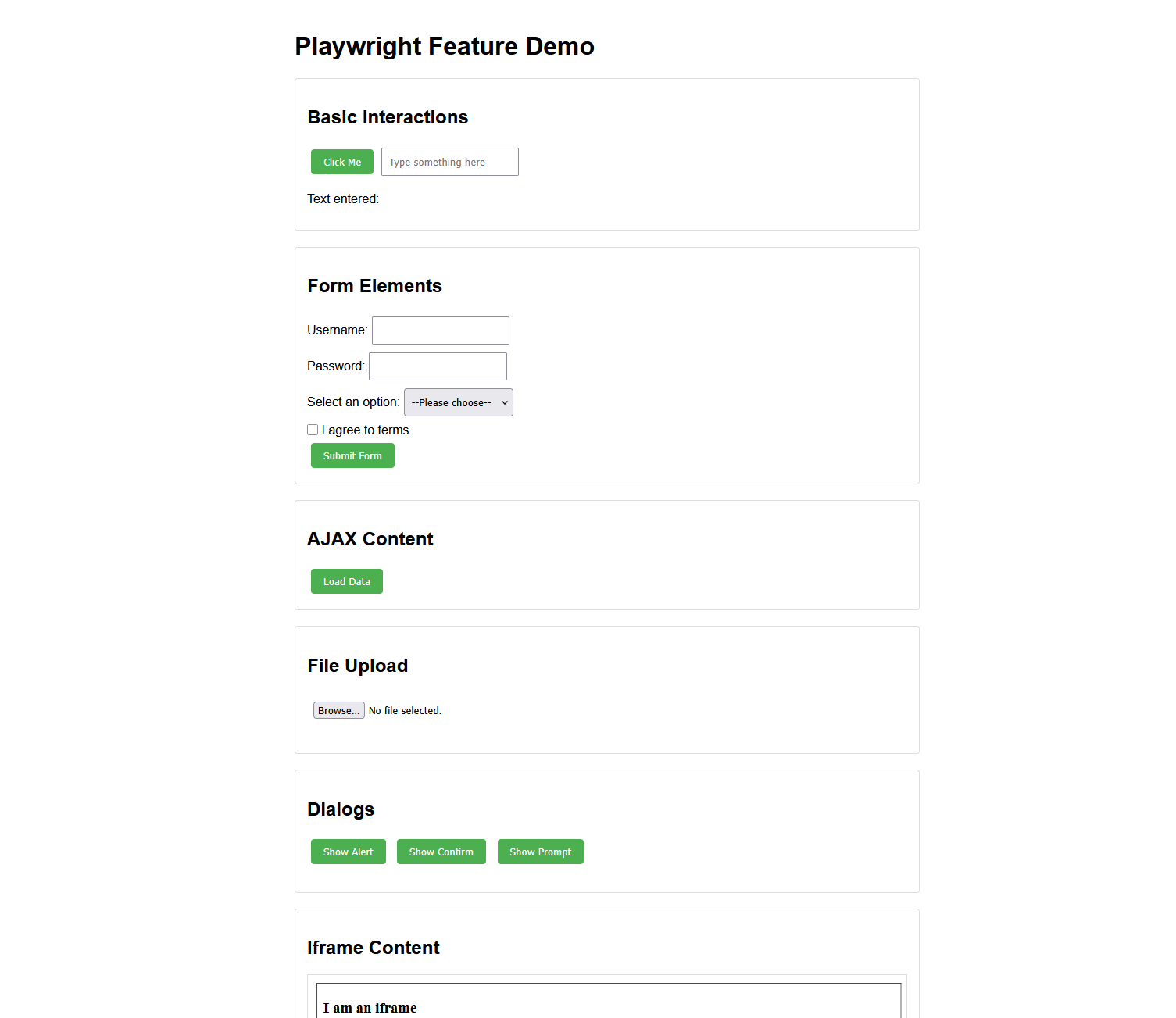
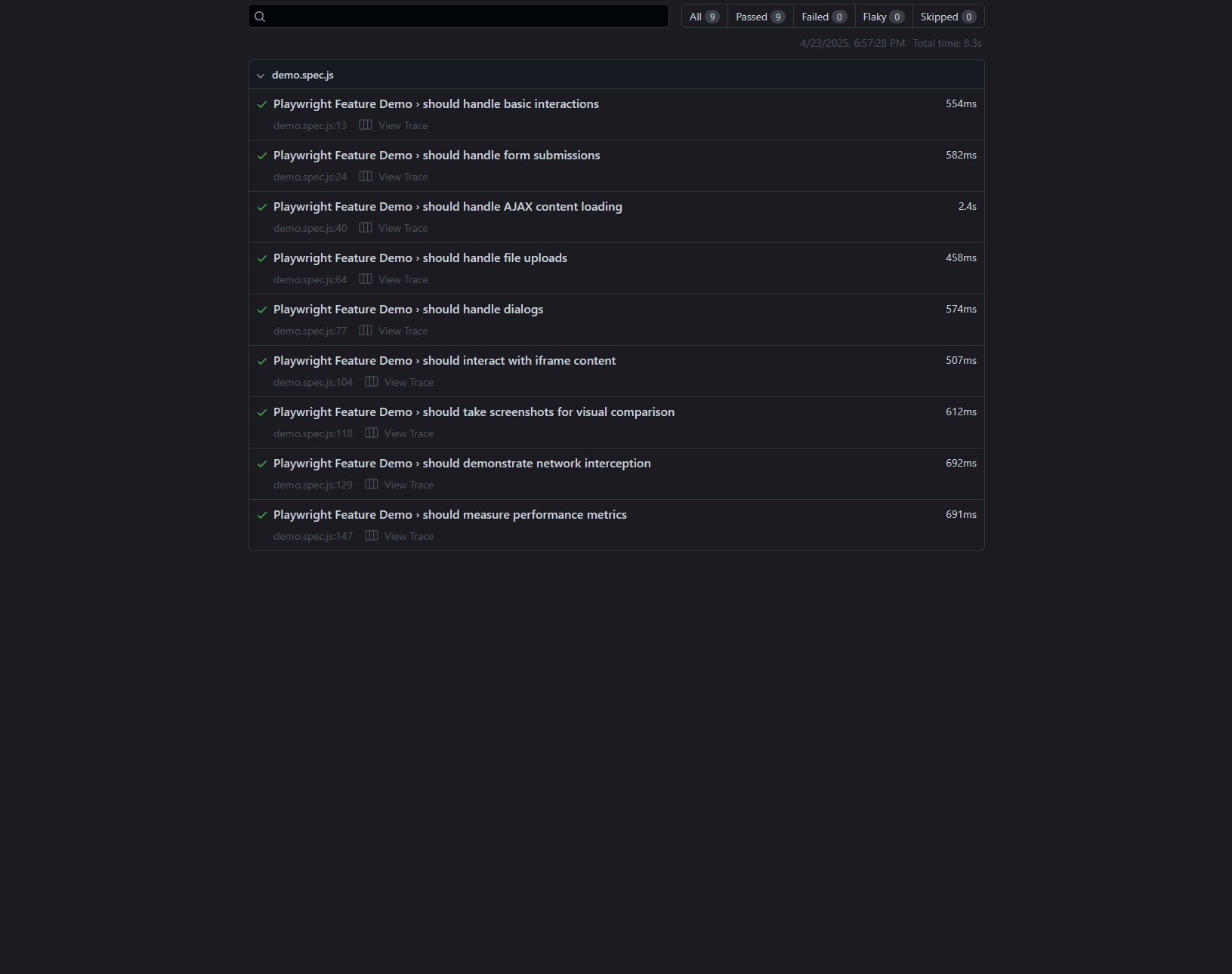
Playwright Demo

This small HTML project was done to create a small demo of the Playwright API for CSCI 5802 - Software Engineering II. It is a simple web application with various buttons and forms, with a testing suite that uses Playwright to test the functionality of the application. There are several different tests run, including AJAX loading, mock API calls, form submission, performance testing, and general button functionality.
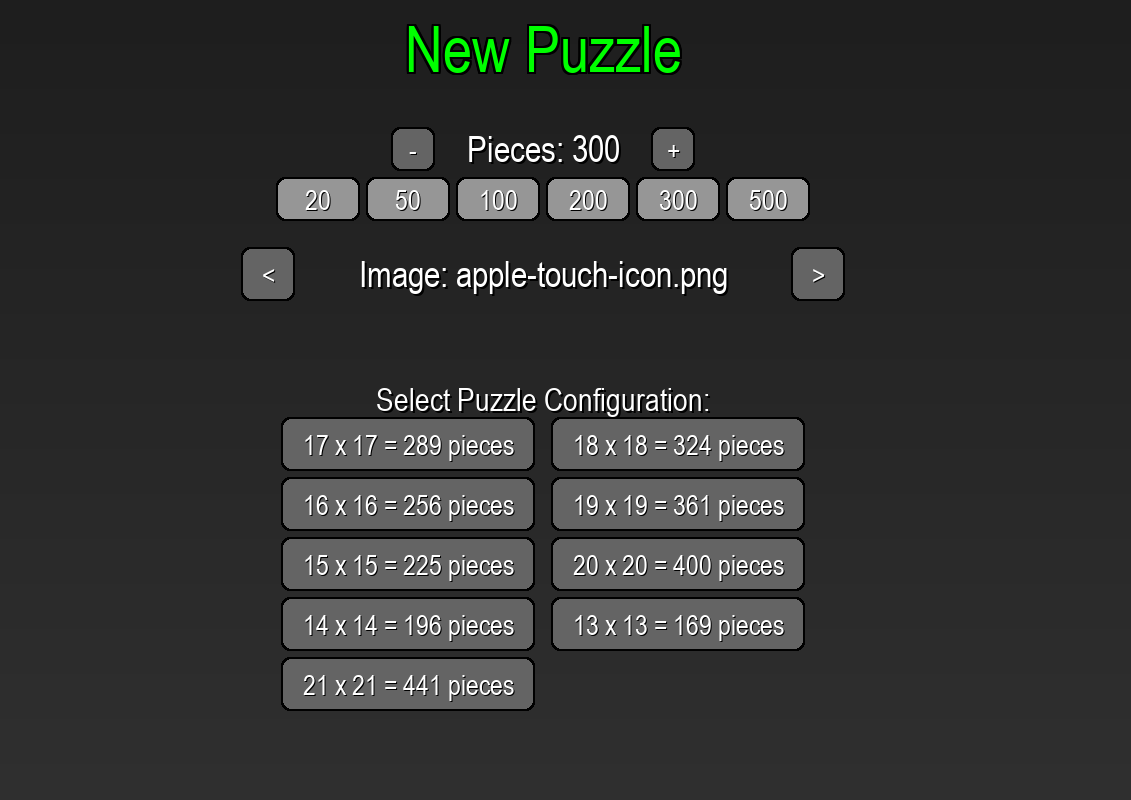
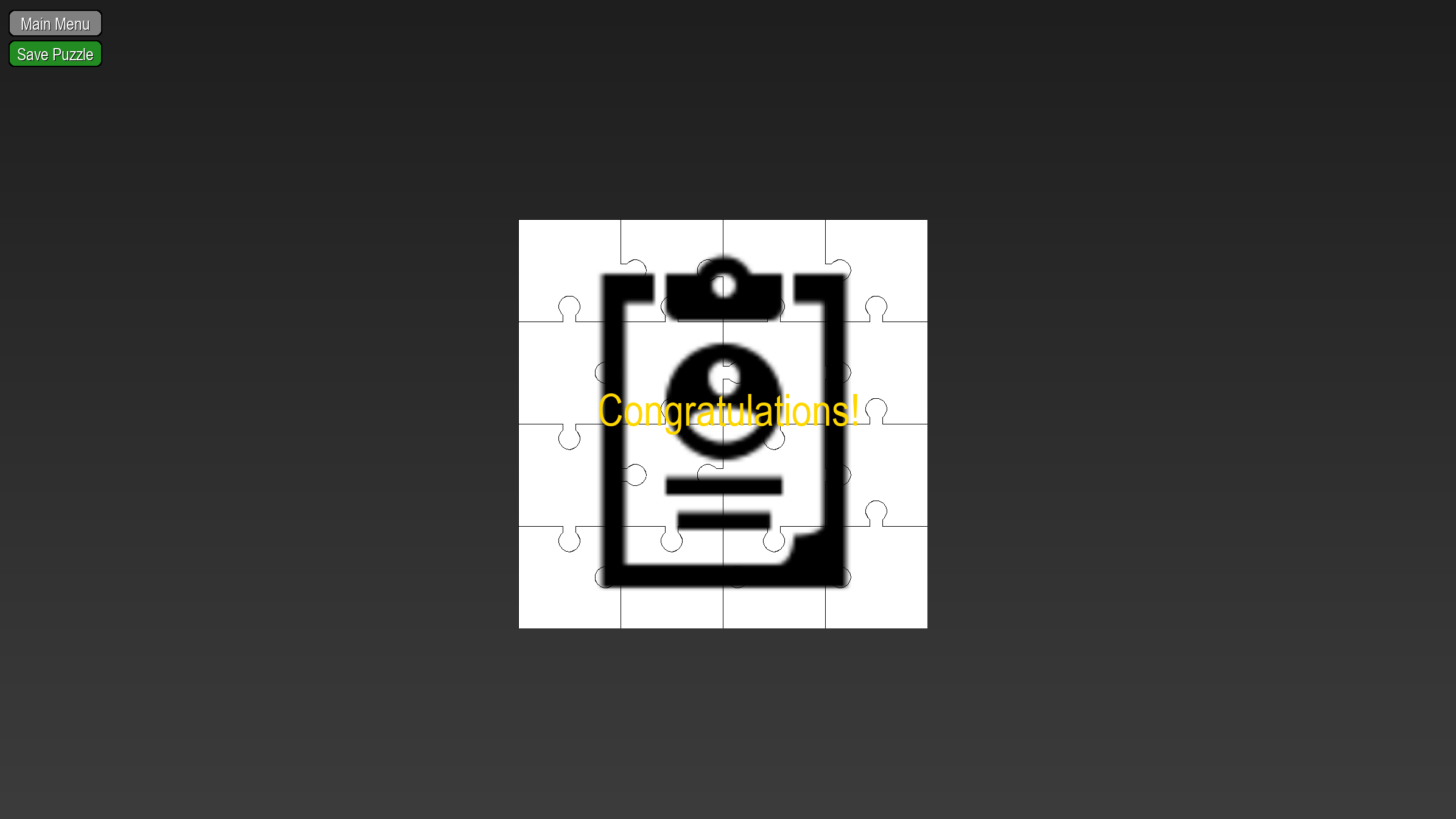
Jigsaw Puzzle Creator
This jigsaw puzzle creator is a Python-based, Pygame powered jigsaw puzzle game that lets players assemble custom images of any size without distortion. It automatically preserves the original aspect ratio when scaling images to the on-screen puzzle area, suggests optimal piece counts and grid configurations based on image dimensions, and offers both manual and preset piece-count selection. When a puzzle is completed, the game reassembles and exports the solved image at full input resolution, complete with precise jigsaw cutout outlines, for an authentic jigsaw experience. This game was created as a way to learn Pygame, and how to work with images in Python.